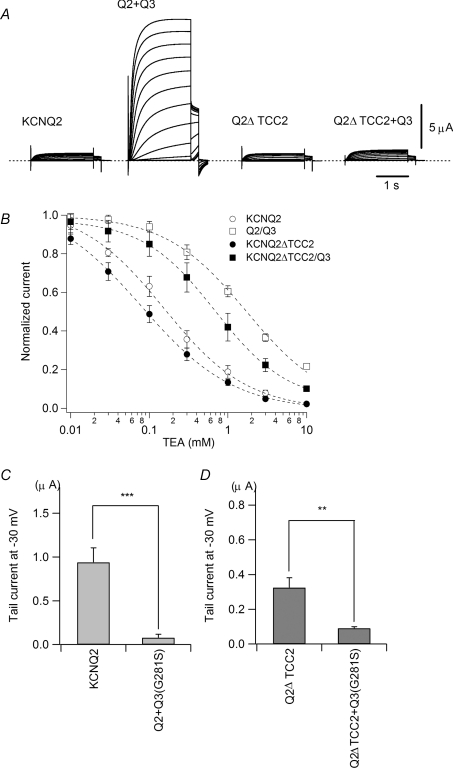
Figure 1. KCNQ2ΔTCC2 cannot induce heteromerization-induced current augmentation with KCNQ3 but can form a heteromultimer with KCNQ3.
A, representative current traces for homomeric KCNQ2, heteromeric KCNQ2/KCNQ3, homomeric KCNQ2ΔTCC2 and heteromeric KCNQ2ΔTCC2/KCNQ3 channels. B, TEA sensitivity of wild-type KCNQ2 and KCNQ2ΔTCC2, with or without KCNQ3 coexpression. C, effect of a KCNQ3 dominant negative mutant (G281S) coexpressed with wild-type KCNQ2. Maximum tail current amplitudes at −30 mV are compared. ***P < 0.001 (Student's t test). D, effect of a KCNQ3 dominant negative mutant (G281S) coexpressed with KCNQ2ΔTCC2. Maximum tail current amplitudes at −30 mV are compared. **P < 0.01 (Student's t test).