Figure 7.
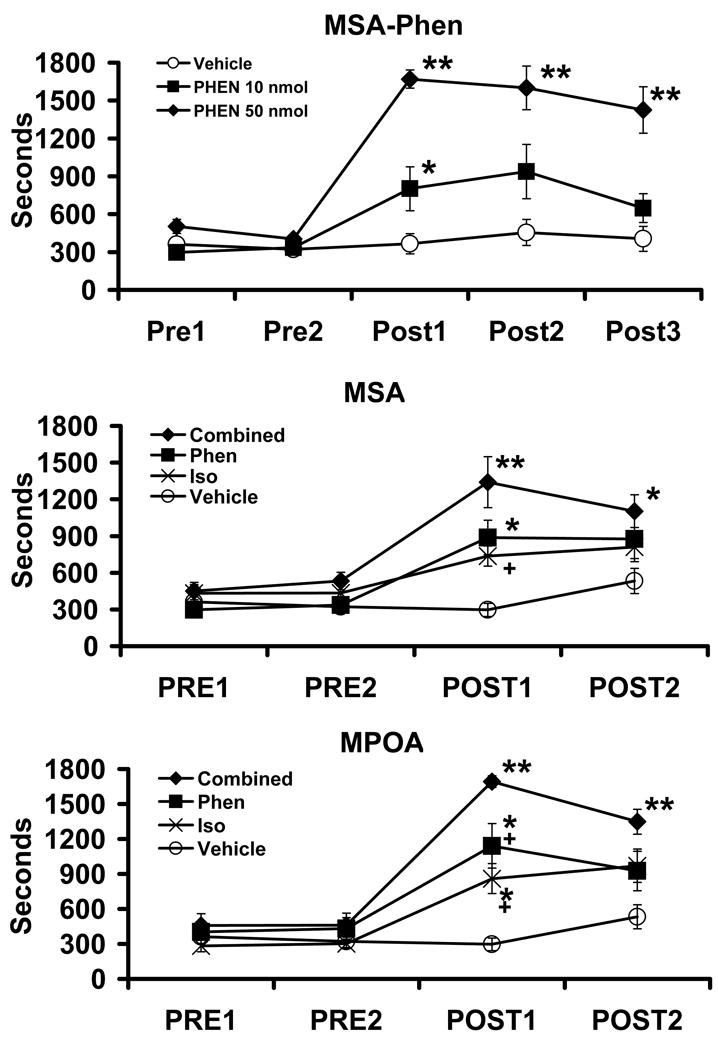
Additive wake-promoting effects of α1- and β-agonist receptor stimulation within the MSA and MPOA. Top Panel depicts dose-dependent wake-promoting actions of infusion of the α1-agonist, phenylephrine (PHEN; 10 nmol, 50 nmol in 150 nl), into the MSA. Intra-MSA infusion produced dose-dependent increases in waking. Middle and bottom panels depict the effects of infusion of vehicle, 10 nmol phenylephrine (Phen), 4 nmol of the β-agonist, isoproterenol (Iso; 4 nmol) and combined phenylephrine and isoproterenol (Combined). For both regions, when administered separately at these doses each drug had a mild wake-promoting action. In the combined treatment group, the wake-promoting effects of isoproterenol and phenylephrine appeared additive and not supra-additive. Symbols represent means (± SEM) of time (secs) spent awake per 30-min testing epoch. PRE1 and PRE2 represent pre-infusion portions of the experiment. POST1-POST3 represent post-infusions epochs. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared to PRE1; +P<0.05 compared to Combined (see [20]).
