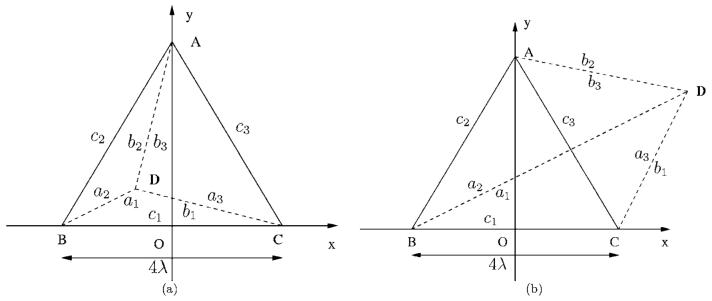
FIG. 2.
Superposition operations that calculate near-field pressures generated by the equilateral triangular source ABC, where each side is 4 wavelengths long. The vertex D (indicated in bold) is the projection of the observation point onto the source plane, which partitions the radiating source into three triangles with sides (ai,bi,ci). (a) The field point is located inside of the equilateral triangular source, and the total field is obtained by adding the contributions from the three triangles that share a vertex at D. (b) The field point is located outside of the equilateral triangular source, and the total pressure is obtained by adding and subtracting the contributions from the three triangles that share a vertex at D.