Fig. 3.
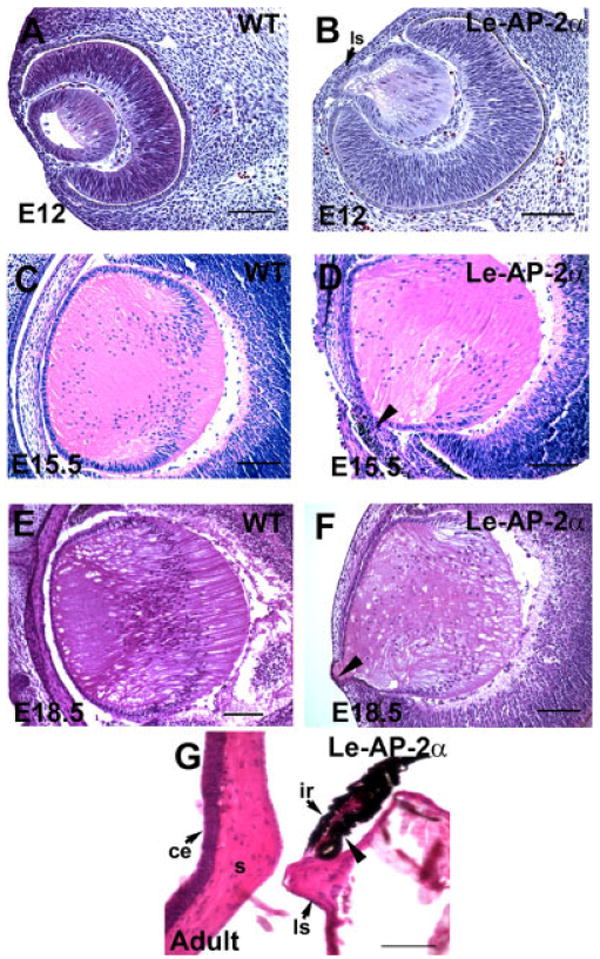
Histological analysis of Le-AP-2α mutant lenses. All panels show hematoxylin and eosin staining of paraffin-embedded sections. A,B: Control (A) and Le-AP-2α (B) mouse eyes at embryonic day (E12) showing that the lens vesicle in Le-AP-2α mice has failed to separate from the surface ectoderm resulting in the formation of a persistent lens stalk. C,D: At E15.5, control eyes (C) develop normally compared to their Le-AP-2α littermates (D) in which pigmentation granules appear in a proportion of cells located within the lens stalk (arrowhead). E,F: At E18.5, control mice (E) develop normally, whereas a lens stalk is observed in Le-AP-2α mice (F, arrowhead). G: Additionally, a proportion of adult Le-AP-2α mutant mice exhibit fusion of the lens to the iris (arrowhead). ls, lens stalk; ce, corneal epithelium; s, corneal stroma; ir, iris. Scale bars = 100 μm.
