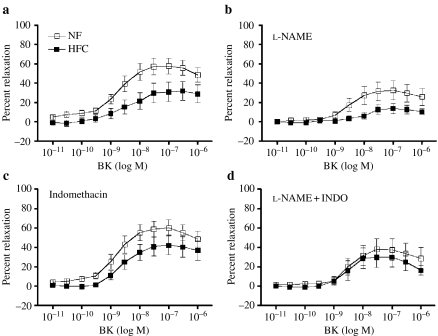
Figure 8.
Dose-dependent, bradykinin (BK)-induced relaxation of left anterior descending coronary arteries. Values are means ± SE. Normal fat (NF) (n = 12 pigs); high fat/cholesterol (HFC) (n = 11). Percent relaxation was calculated as percent reduction in force from PGF2-α (30 M)-induced tension. (a) BK-induced relaxation was impaired in HFC at intermediate and high doses of BK (P < 0.05). (b) Effects of NG-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) on relaxation. (c) Effects of indomethacin (INDO) on relaxation. (d) Effects of l-NAME plus INDO on relaxation. Mixed-factor anova indicated that l-NAME significantly inhibited BK-induced relaxation.