Figure 5.
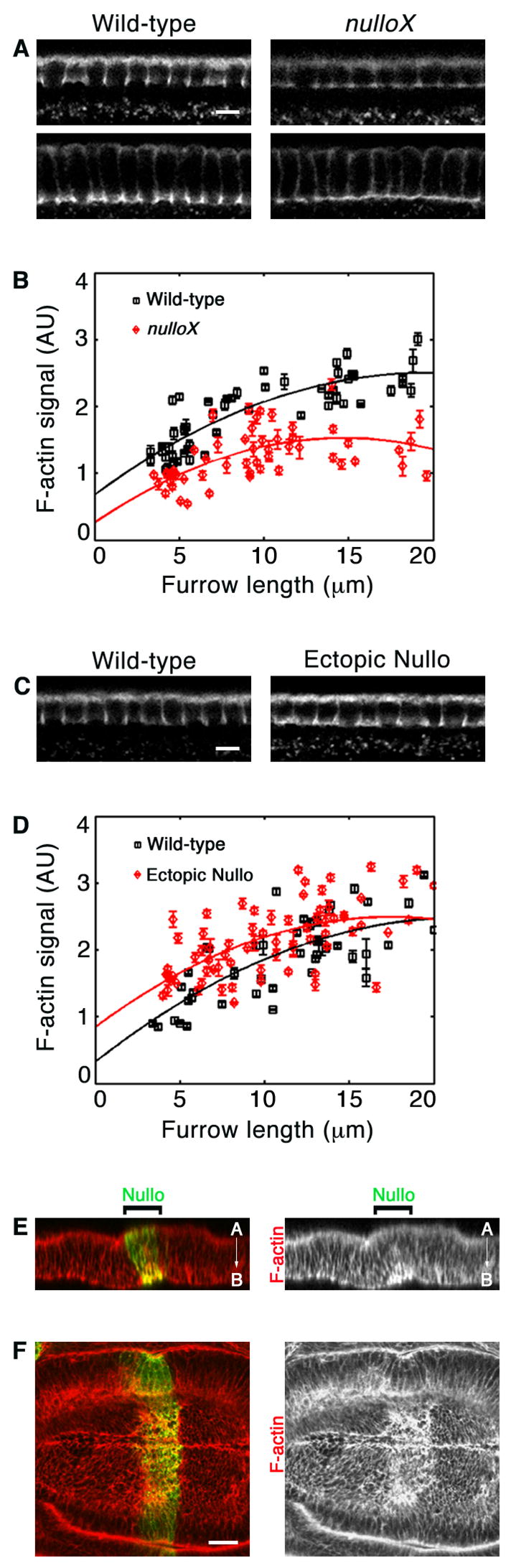
Nullo regulates cortical F-actin. (A, C) Cross-sections of F-actin in comparably staged cellularizing embryos. Images collected at same settings for wild-type versus nullo manipulation. (A) nulloX furrow canals show reduced F-actin. (B) F-actin in wild-type (black) versus nulloX (red) furrow canals, measured by intensity of phalloidin staining. Each point represents one embryo with 75–100 furrow canals analyzed. Error bars show standard deviation. (C) Ectopic Nullo furrow canals show increased actin. (D) F-actin in wild-type (black) versus ectopic Nullo (red) furrow canals, quantified as in B. (E–F) F-actin (red) in an imaginal wing disc expressing a stripe of ectopic Nullo (green). (E) Projected Z-section shows that F-actin is increased at basal-lateral cortex of Nullo-expressing cells (A, apical; B, basal). (F) En face image from a single basal plane of the disc showing a stripe of F-actin increase in Nullo-expressing cells. Bars are 5 μm in A and C, and 20 μm in F.
