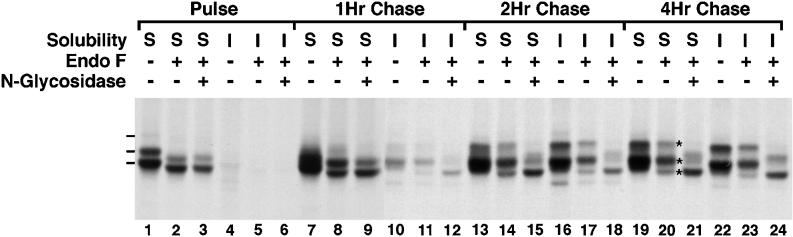
Figure 1.
Posttranslational modification and detergent insolubility of AE1 anion exchangers. Erythroid cells from a 10-d-old chicken embryo were pulsed with 35S-Translabel in methionine-free DMEM for 15 min at 37°C. At the end of the pulse (lanes 1–6) an aliquot of cells was lysed in isotonic buffer containing 1% Triton X-100. The lysate was separated into soluble (S) and insoluble (I) fractions by centrifugation. The remainder of the cells were incubated at 37°C in DMEM containing 10% FCS for 1 h (lanes 7–12), 2 h (lanes 13–18), or 4 h (lanes 19–24), and at each time point the cells were fractionated as described above. Immunoprecipitates prepared from the soluble and insoluble fractions using AE1-specific peptide antibodies were either undigested, digested with endo F, or digested with endo F followed by digestion with N-glycosidase. Immune complexes were analyzed on a 6% SDS polyacrylamide gel, and labeled anion exchangers were detected by fluorography. Dashes adjacent to lane 1 mark the 97-, 100-, and 108-kDa AE1 polypeptides in the detergent-soluble fraction at the pulse point. Asterisks adjacent to lane 20 mark the detergent-soluble AE1 polypeptides of 95, 98, and 105 kDa detected at the 4-h chase point after endo F digestion.