Figure 8.
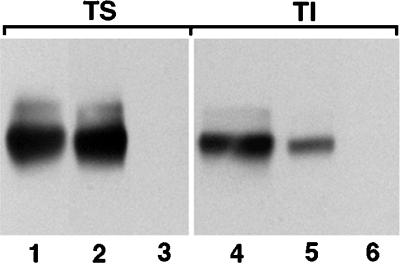
Susceptibility of detergent-soluble and detergent-insoluble AE1 to surface biotinylation. Erythroid cells from a 10-d-old chicken embryo were cell surface biotinylated by incubating with 1 mg NHS-SS-Biotin/ml in Ringer’s buffer for 30 min at 4°C. The cells were then washed in Ringer’s buffer and detergent lysed by incubating in isotonic buffer containing 1% Triton X-100. The lysate was separated into soluble (TS) and insoluble (TI) fractions by centrifugation, and biotinylated polypeptides were precipitated using streptavidin agarose. Streptavidin-precipitable material was analyzed on a 6% SDS polyacrylamide gel, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with an AE1-specific antibody. After washing, the blot was incubated with goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase, and immunoreactive species were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence. Lanes 1 and 4 correspond to the total detergent-soluble and detergent-insoluble fractions, respectively, from 105 erythroid cells. Lanes 2 and 5 correspond to the streptavidin-precipitable polypeptides from the soluble and insoluble fractions of an equivalent number of cells. Lanes 3 and 6 are controls that were processed identically to lanes 2 and 5 except the cells were not biotinylated before lysis and streptavidin precipitation.
