Abstract
Colicinogenic factors ColE1 and ColE2 are bacterial plasmids that exist in Escherichia coli as supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and as strand-specific, relaxation complexes of supercoiled DNA and protein. Newly replicated ColE1 DNA becomes complexed with protein after the replication event. This association of DNA and protein can take place under conditions in which DNA or protein synthesis is arrested. The addition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (c-AMP) to normal cells growing in glucose medium results in a six- to tenfold stimulation in the rate of synthesis of the protein component(s) of the complex and a three- to fivefold stimulation in the rate of ColE1 DNA replication. Employing mutants deficient in catabolite gene activator protein or adenylate cyclase, it was shown that synthesis of both the plasmid-determined protein colicin E1 and the protein component(s) of the ColE1 relaxation complex is mediated through the c-AMP-catabolite gene activator protein system. Addition of c-AMP to ColE2-containing cells results in the stimulation of synthesis of ColE2 DNA and relaxation protein(s) as well as in the production of a protein component of the ColE2 relaxation complex that renders it sensitive to induced relaxation by heat treatment. In the case of ColE2, synthesis of the relaxation protein(s) is not dependent upon catabolite gene activator protein.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. B., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Effect of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate analogues on the activity of the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2717–2722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Helinski D. R. Circular DNA forms of colicinogenic factors E1, E2 and E3 from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 14;36(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90374-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Clewell D. B., Sheratt D. J., Helinski D. R. Strand-specific supercoiled DNA-protein relaxation complexes: comparison of the complexes of bacterial plasmids ColE1 and ColE2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
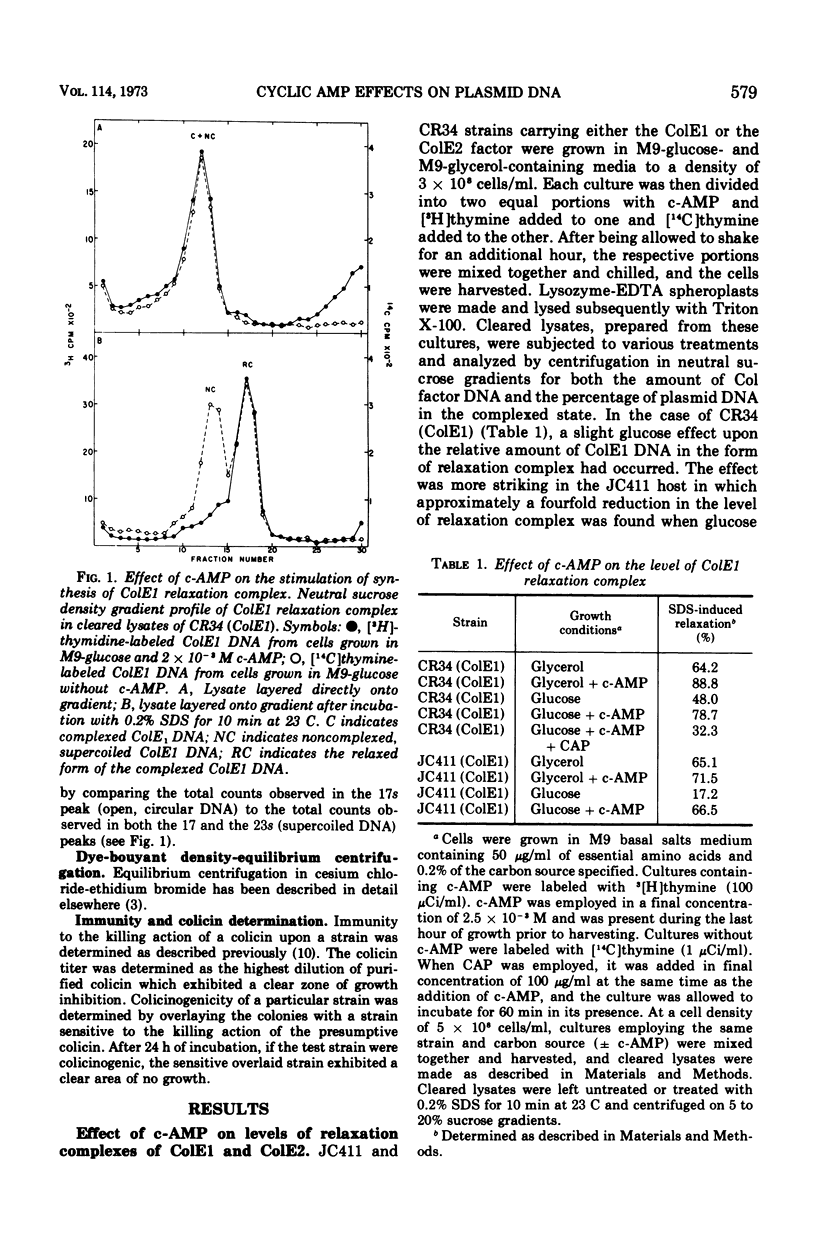
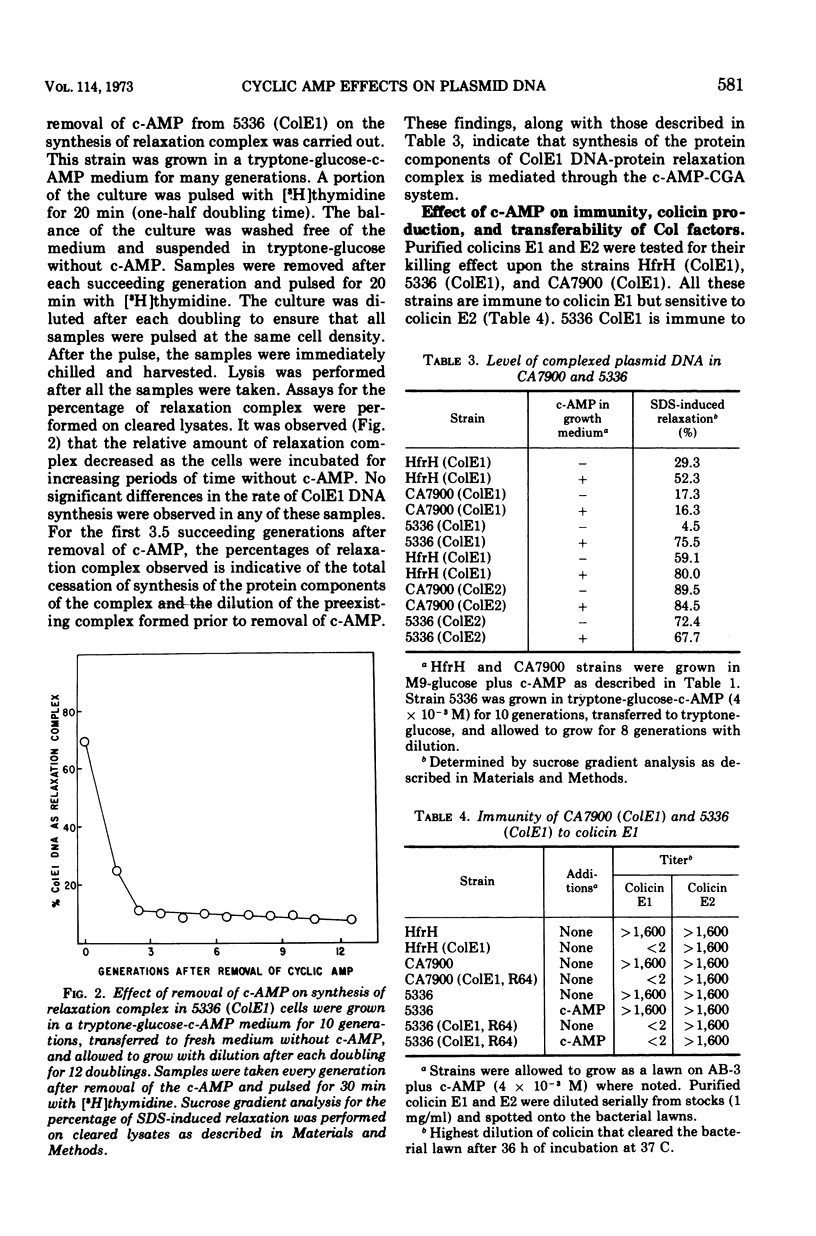
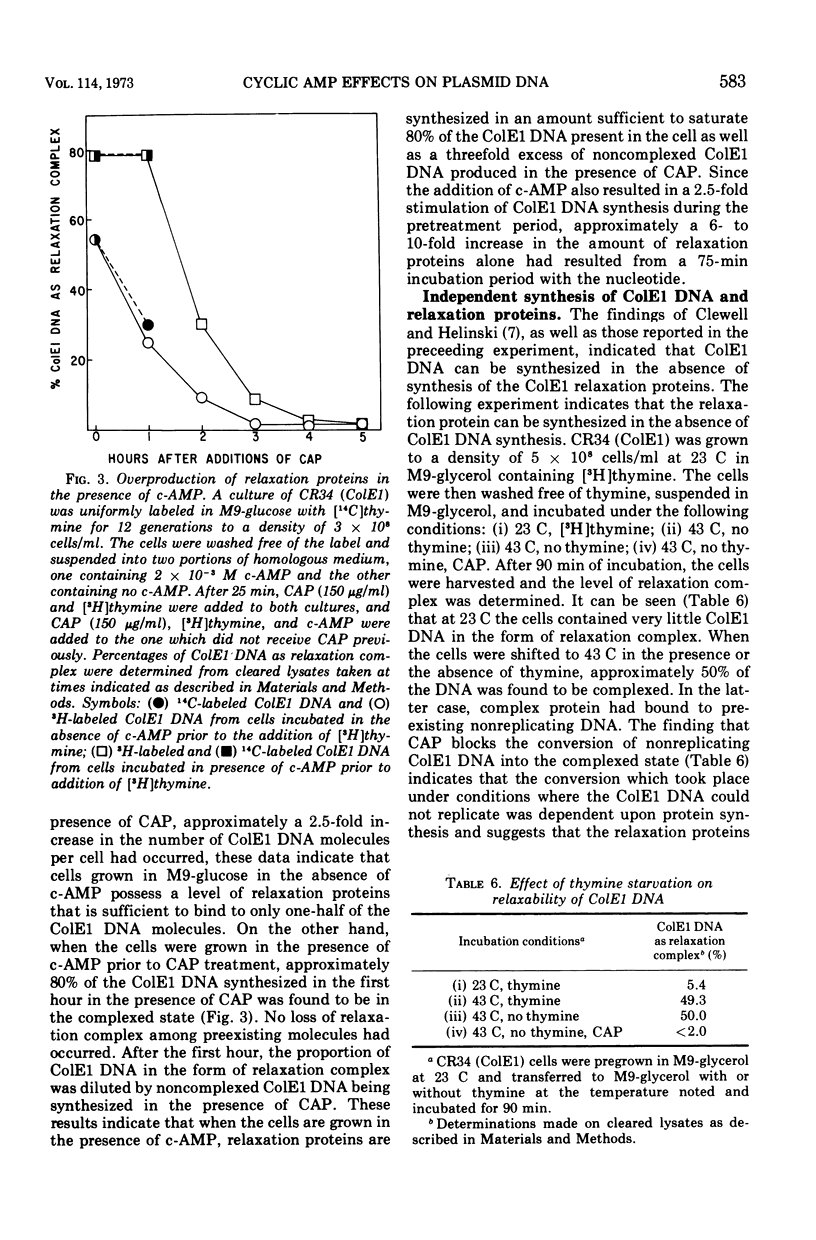
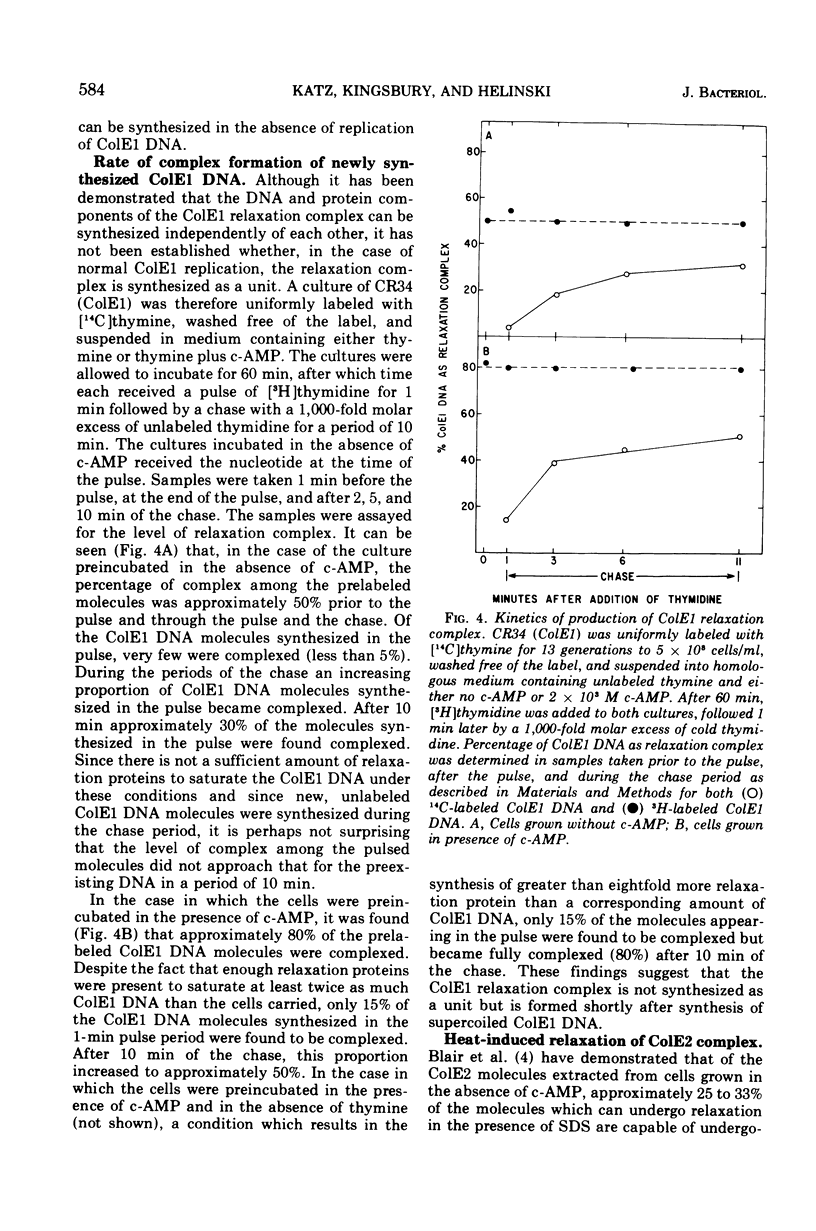
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmer M., deCrombrugghe B., Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic AMP receptor protein of E. coli: its role in the synthesis of inducible enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):480–487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R., Helinski D. R. Comparative study of the events associated with colicin induction. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):691–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.691-699.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHN P., HELINSKI D. R. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN COLICINOGENIC FACTORS E1 AND V AND AN F FACTOR IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1573–1579. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1573-1579.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Englesberg E. Hyperinducibility as a result of mutation in structural genes and self-catabolite repression in the ara operon. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):34–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.34-52.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN R. S., SUTHERLAND E. W. ADENOSINE 3',5'-PHOSPHATE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1309–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisseley S. P., Anderson W. B., Gottesman M. E., Perlman R. L., Pastan I. In vitro transcription of the gal operon requires cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4671–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman R. L., Pastan I. Pleiotropic deficiency of carbohydrate utilization in an adenyl cyclase deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90893-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Reiness G., Zubay G. Purification and DNA-binding properties of the catabolite gene activator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1222–1225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. A., Helinski D. R. Purification and characterization of colicin E1. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6318–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Schwartz D., Beckwith J. Mechanism of activation of catabolite-sensitive genes: a positive control system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):104–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


