Figure 2.
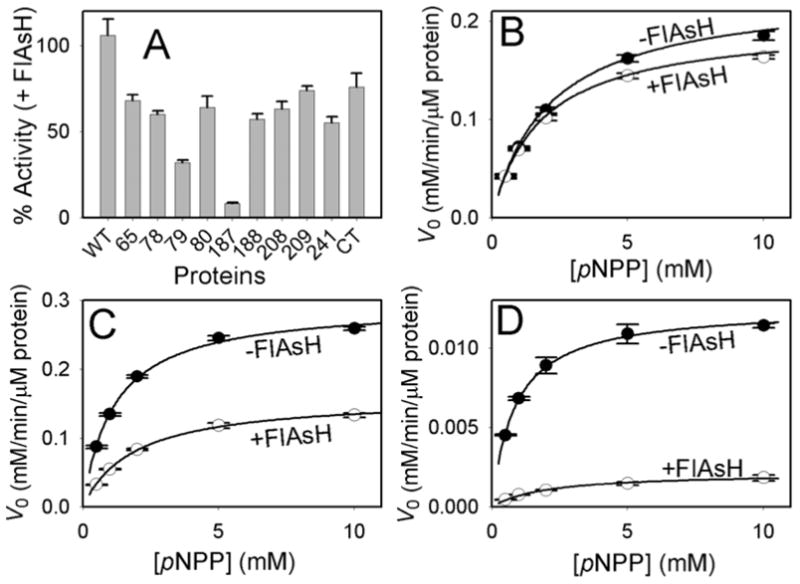
FlAsH-dependent inhibition of TCPTP insertion mutants. (A) The indicated TCPTP enzymes (2.5 μM) were incubated in the absence or presence of FlAsH (10 μM), diluted and assayed for activity with the artificial PTP substrate para-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) at pH 7.0. “% Activity” represents the PTP catalytic efficiency (kcat/KM) in the presence of FlAsH divided by the control (no-FlAsH) catalytic efficiency of the same TCPTP enzyme. (B-D) Allosteric inhibition of TCPTP-79 and TCPTP-187 by FlAsH. The initial rates of wild-type TCPTP (B), TCPTP-79 (C), and TCPTP-187 (D) were measured at the indicated pNPP concentrations in the absence and presence of FlAsH as described in A.
