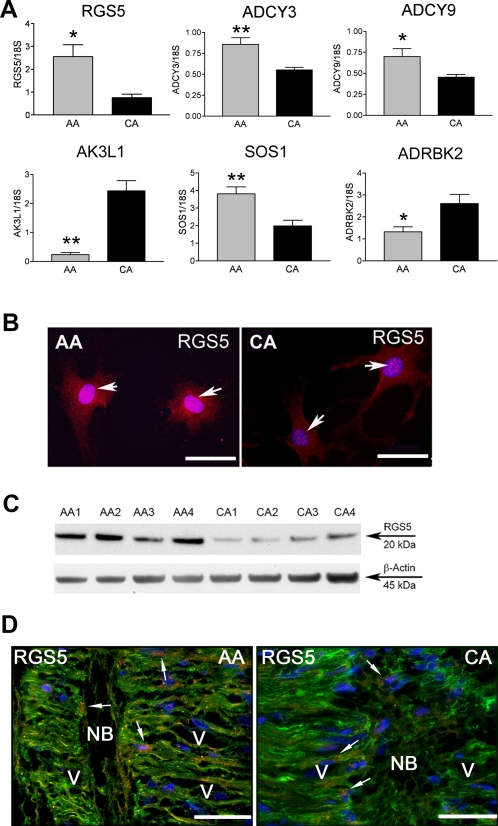
Figure 2. Signal transduction pathways in AA astrocytes compared to CA astrocytes.
A. Confirmation of six differentially expressed signaling genes by qRT-PCR in human normal ONH astrocytes: RGS5, ADCY3, ADCY9, AK3L1, SOS1 and ADRBK2. Genes were normalized to 18S. Graphical representation of the relative mRNA levels in normal AA and CA astrocytes (n = 8, respectively, two-tailed t test was used. **indicates p<0.01 and * indicates p<0.05). B. Cellular localization of the Regulator of G protein signaling 5 (RGS5) in primary cultures of ONH astrocytes. Immunofluorecent staining of RGS5 (red) demonstrated higher levels of RGS5 protein in AA astrocytes, compared to CA astrocytes. Nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). Note that RGS5 localizes to the cytoplasm and in the nucleus of astrocytes (arrows). Magnification bar: 25 µm. C. Representative Western blots of astrocyte cell lysates with human RGS5 antibody and β-actin used as a loading control. Note that AA1-4 normal donors express more RGS5 than CA1-4 donors. D. Representative double immunofluorescent staining of RGS5 (red) astrocyte marker GFAP (green) in sections of human ONH from an AA donor (71 year-old male) and a CA donor (75 year-old male). Nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). Note strong granular staining of RGS5 in astrocytes (arrows) in the cribriform plates in the lamina cribrosa. Fewer astrocytes stain for RGS5 in the lamina cribrosa of a CA donor. V: blood vessel, NB: nerve bundle, Magnification bar 55 µm.