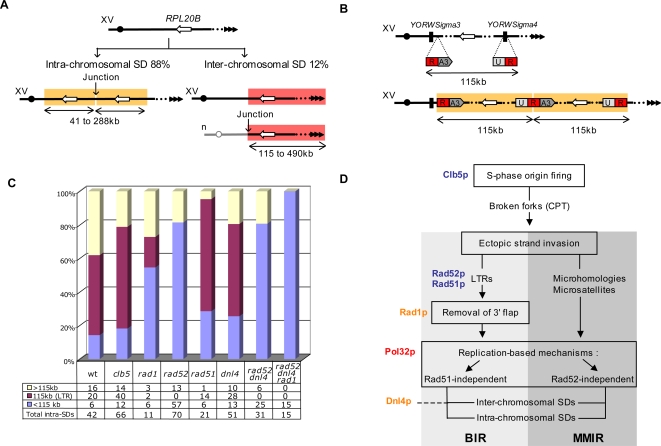
Figure 1. Segmental duplication assays.
(A) Growth recovery assay [20]. Black circles and triangles represent centromeres and telomeres, respectively. White open arrow represents the RPL20B gene (YOR312C) whose duplication is selected for. Yellow and pink boxes denote intra- (left) and one type of inter-chromosomal (right) duplications, respectively. A non-reciprocal translocation event between the right arm of chromosome XV and another chromosome (denoted “n”) is represented: for other types of inter-chromosomal SD (i.e. chimerical supernumerary chromosome and unequal reciprocal translocation, see [20] and [21]). SD size ranges are indicated below the double-headed arrows. (B) Uracil prototrophy recovery assay. Top: schematic representation of the right arm of chromosome XV spanning the RPL20B locus and the two flanking Ty3 LTRs (YORWsigma3 and YORWsigma4) located 115 kb apart from each others. 5′- and 3′-truncated are either inserted next (YORWsigma3) or replaces (YORWsigma4) Ty3 sequences. The “R”-labeled red box indicates the 58 or 401 bp overlap between the two truncated URA3 cassettes. Bottom: a functional URA3 gene restoring uracil prototrophy is generated through 115 kb direct-tandem duplication events involving the overlapping sequences. (C) Size distribution of intra-chromosomal SDs. The x and y-axis of the diagram indicate the strain background and the percentage of events recovered, respectively. Yellow, violet and blue bars represent the proportion of duplications larger, equal to and smaller than 115 kb, respectively (with the actual number of events analyzed indicated in the table below). (D) Phenomenology of SD formation. Protein names involved in the different steps are indicated to the left of the diagram. Red, orange and blue names represent proteins whose deletions abolish, reduce and increase SD formation, respectively. Light and medium grey boxes indicate the two alternative mechanisms of SD formation, BIR (Break-induced Replication) and MMIR (Microhomology/Microsatellite-induced Replication), respectively. CPT = camptothecin.