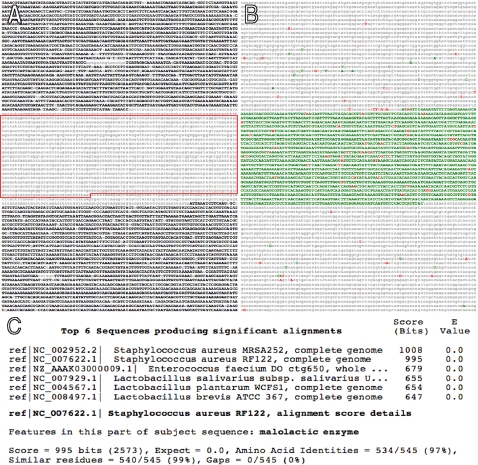
Figure 2. EvoPrint and EvoUnique comparative analysis of 13 different S. aureus isolates reveals that only the human MRSA252 and contagious bovine mastitis RF122 chromosomes contain the malolactic enzyme gene.
A) An EvoPrint generated from pairwise alignments of MRSA252 DNA (6,497 bp) and aligning regions from 12 other S. aureus genomes (S. aureus COL; S. aureus MSSA476, S. aureus Mu50; S. aureus MW2; S. aureus N315; S. aureus NCTC 8325; S. aureus RF122; S. aureus USA300; S. aureus JH1; S. aureus JH9; S. aureus Mu3 and S. aureus Newman) reveals high homology between all aligning regions except for a central 1,981 bp region. Uppercase black-colored letters identify MRSA252 sequences that align with all genomes and lowercase gray-colored bases indicate nucleotides that do not align with at least one of the genomes. The boxed ORF sequence encodes the 545 amino acid malolactic enzyme. B) Generated from the same analysis, the MRSA252 EvoUnique print indicates that only one of the 12 genomes included in the analysis contains homologous sequences that span the MRSA252 malolactic enzyme gene locus (SAR0824). Uppercase red-colored SNPs are unique to the MRSA252 sequence; green-colored letters represent bases that align with only one of the 12 genomes (S. aureus RF122) and lowercase gray-colored letters represent sequences that are common to two or more alignments. (C) Protein database homology searches identify the RF122 malolactic enzyme as sharing the highest identity with the MRSA252 enzyme. Note: no homologies to other malolactic enzyme encoding genes were detected in other S. aureus species.