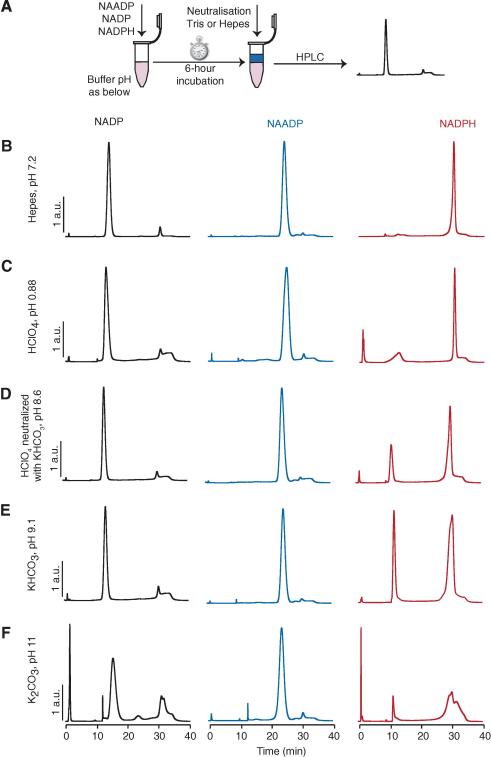
Fig. 2.
Stability of nucleotides during the acid extraction procedure. (A) Schematic showing the procedure. NAADP, NADP, or NADPH (1 mM) was incubated for 6 h in the solutions indicated. Samples were then neutralized by the addition of Hepes acid for basic samples, or Tris base for acidic samples, and were analyzed by HPLC. HPLC traces show the stability of NAADP, NADP, and NADPH in Hepes (pH 7.2) (B), HClO4 (pH 0.88) (C), HClO4 neutralized with KHCO3 (pH 8.6) (D), KHCO3 (pH 9.1) (E), and K2CO3 (pH 11) (F). HPLC traces are scaled to a common peak height for comparison (maximum 20% scaling). Note that NADP is stable except at pH 11, when a number of products result; in particular, NAADP is generated, and this would interfere with correct determination of NAADP levels from a cell extract. NADPH is stable only at pH 7.2, but NADP is the principal breakdown product; NAADP is not produced under the conditions tested. a.u., arbitrary unit.