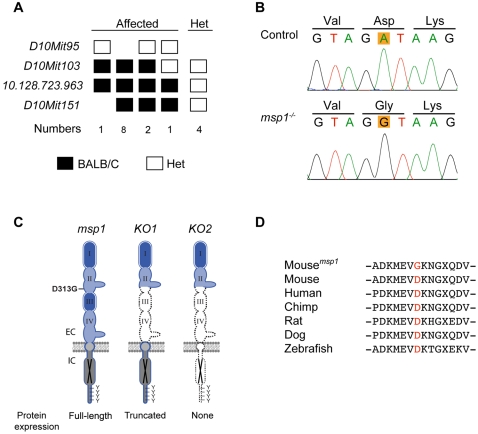
Figure 2. Linkage Analysis and Molecular Characterization of the msp1 Mutation.
(A) Fine mapping of the msp1 locus on mouse Chr 10. The mutation is confined within a region distal to D10Mit103. The number of affected mice analyzed is shown below genotyping data (homozygote black square; heterozygote white square). (B) Sequencing results of Erbb3 from control and msp1 embryos. The msp1 embryos carry an A-to-G transition in exon 8 of the Erbb3 gene that results in change of the aspartic acid (D) to glycine (G) at position 313. (C) Position of the msp1 mutation (D313G) in the ERBB3 protein. The ERBB3 protein consists of an extracellular region (EC), a single transmembrane-spanning region, and an intracellular (IC) portion that contains a conserved tyrosine-kinase domain flanked by a carboxy-terminal tail with tyrosine phosphorylation sites. The extracellular region is further subdivided into four domains: domain I, II, III, and IV. Domains I and III are homologous; domains II and IV are homologous. ERBB3 is a kinase-deficient receptor (black X). The D313G is located in the domain II (also known as cysteine-rich region I (CR1)) of ERBB3. In Erbb3KO1 allele a large portion of the extracellular domain is deleted, thus forming a truncated ERBB3 protein. In Erbb3KO2 allele no protein is made due to the insertion of premature termination codons in all three reading frames. (D) Multiple sequence alignment of Erbb3 from various species. The substituted aspartic acid (D313) is highly conserved among different species.