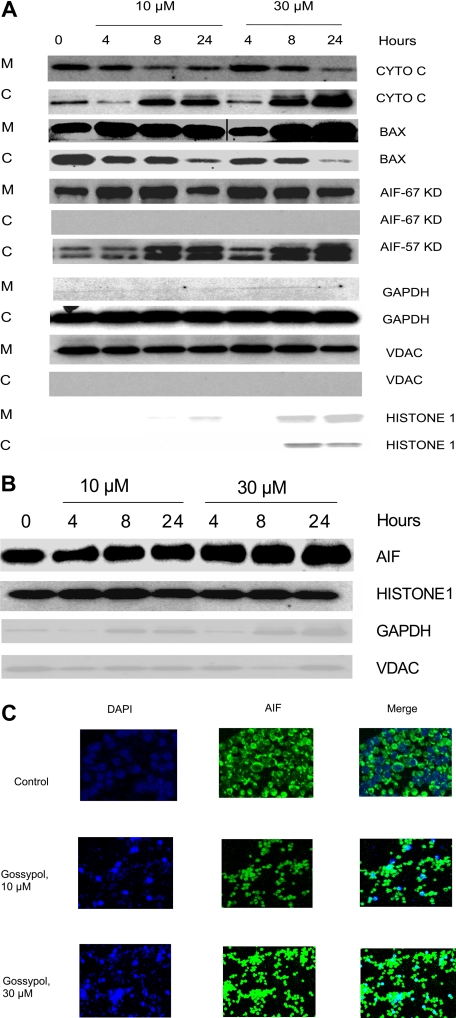
Figure 6.
Effect of gossypol on release and translocation of proapoptotic proteins. (A) Gossypol induces the release of proapoptotic proteins in CLL primary cells. CLL primary cells were treated with 10 μM or 30 μM gossypol for indicated hours, and the expression of cytochrome c (CYTO C), BAX (in mitochondrial BAX, the last 3 lanes were spliced from the same gel which was originally loaded on the first 3 lanes. A vertical line is inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane, and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) ∼57-kDa (amino acids-1-300) and AIF ∼67-kDa (amino acids 517-531) were analyzed. GAPDH, VDAC, and Histone 1 (cytosolic, mitochondrial, and nuclear loading controls, respectively) were evaluated by immunoblotting in cytosolic (C) and mitochondrial (M) fractions. Similar experiments were done in 5 patients, and the immunoblot from 1 representative patient is provided. (B) Translocation of AIF to the nucleus in gossypol-treated CLL primary cells. CLL primary cells were treated with 10 μM or 30 μM gossypol for 4, 8, and 24 hours, and the expression of AIF (the last lane is spliced from the same gel which was originally loaded on lane 8) was analyzed in the nuclear fraction by immunoblotting. GAPDH, VDAC, and histone 1 (cytosolic, mitochondrial, and nuclear loading controls, respectively) were used as loading controls. (C) CLL primary cells were incubated with 10 μM and 30 μM gossypol for 24 hours, stained with anti-AIF antibody, and then subjected to fluorescent staining with DAPI (nuclear staining, blue) and FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (green), and the images were captured on confocal microscopy.