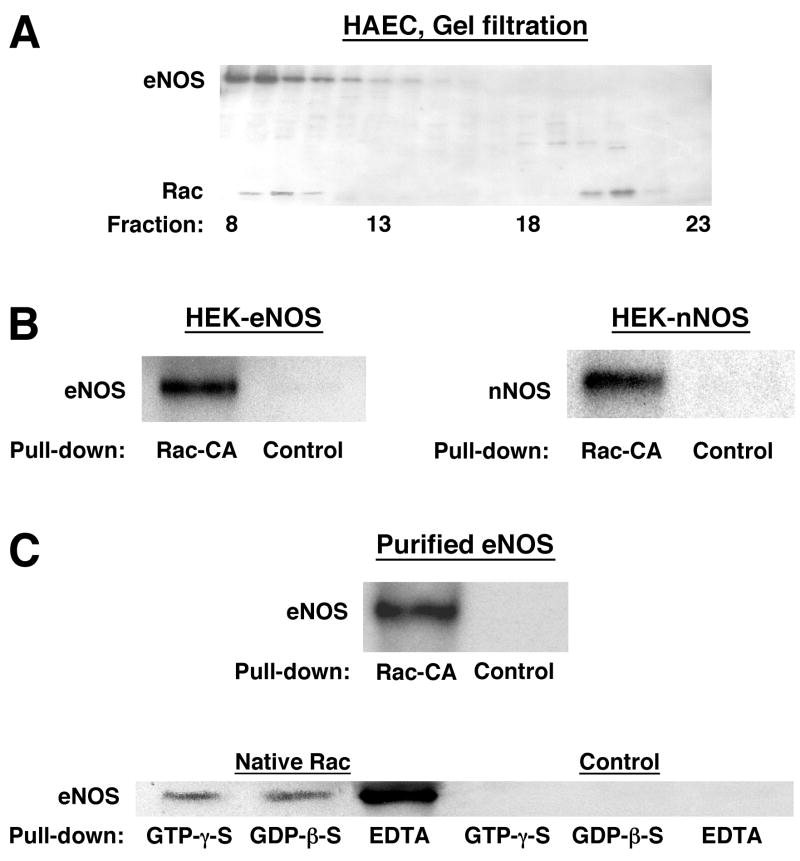
Fig. 3.
Molecular interaction of Rac and NOS. (A) Rac and eNOS co-elute, in size-exclusion chromatography (Superdex-200) of HAEC extracted with 1% NP-40, in high-mass complexes (fraction 10 ≈ 650 kDa) and a population of Rac elutes independently of eNOS (fraction 21 ≈ 18 kDa, consistent with uncomplexed, monomeric Rac). The western blot shown was reacted with antibodies to Rac and eNOS simultaneously. (B) GST-Rac-CA bound to glutathione-sepharose complexes with eNOS and with nNOS in extracts of NOS-transfected HEK cells and with eNOS in extracts of HAEC. Control samples (B and C) were generated by incubating equal quantities of extract (or of purified eNOS) with GST-bound glutathione-sepharose. (C) Purified eNOS binds directly to immobilized Rac-CA and wild-type Rac. Binding of eNOS to GTP- vs. GDP-bound Rac is indistinguishable, and binding of eNOS to nucleotide-free Rac (EDTA) is substantially more efficient.