Figure 4.
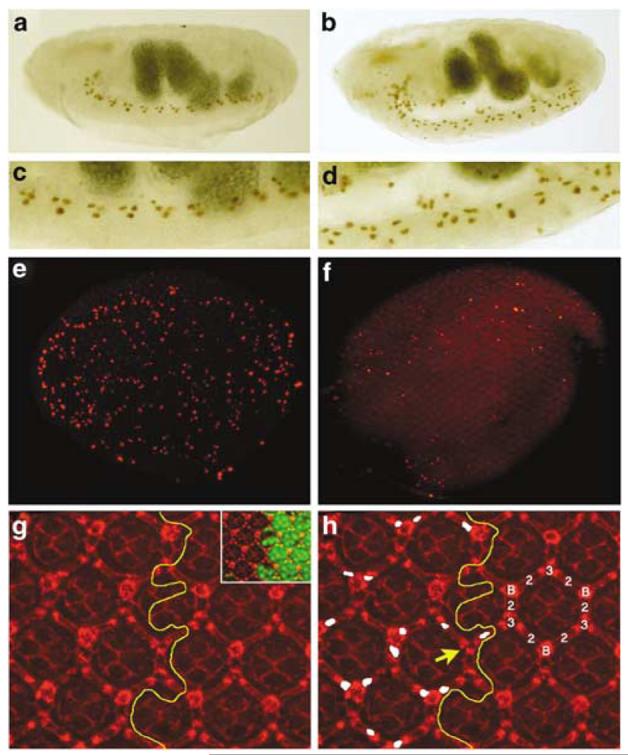
drICE17 mutants contain additional cells. (a) The midline glia (MG) of a stage 17 wild-type embryos visualized by a P[sli-1.0]lacZ reporter transgene. (b) The MG of stage 17 drICE17 embryos contains additional cells. (c) Enlargement of the ventral nerve cord of the wild-type embryo in (a). (d) Enlargement of the ventral nerve cord of the drICE17 mutant in (b). (e) Whole mount of a wild-type pupal eye disc 26 h APF labeled for TUNEL. (f) Whole mount of a drICE17 mutant eye disc 26 h APF labeled for TUNEL. The global cell death pattern is reduced compared to (e). (g and h) IOC survival in drICE17 mutant clones. (g) Overview of a Dlg-labeled (red) drICE17 mosaic eye disc 42 h APF to visualize the weak disorganization of the mutant lattice. The yellow line marks the clonal boundary. The inset shows the drICE17 clone marked by absence of GFP (green). (h) Shows the same field as (g). The interommatidial cell (IOC) cluster is composed of six secondary (2), three tertiary (3) and three bristle cells (B). The yellow line marks the clonal boundary. Extra IOCs in the drICE17 clone are marked in white. The yellow arrow points to a rare patterning defect in which a bristle cell is replaced by a tertiary pigment cell
