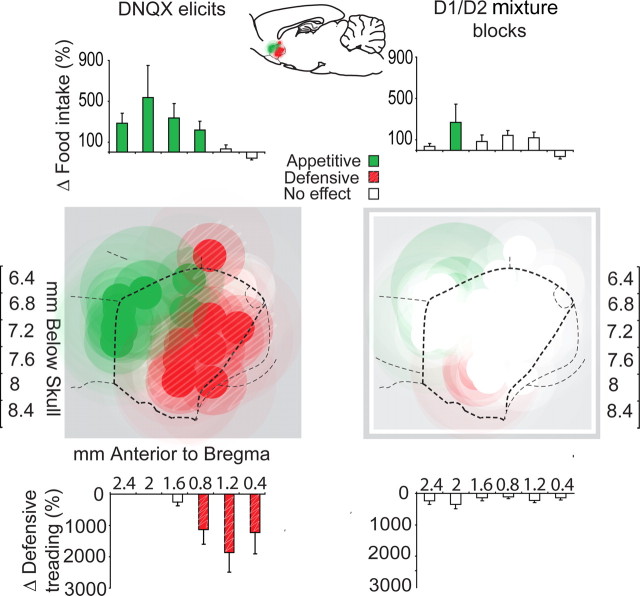
Figure 4.
Summary map of “desire versus dread” motivations produced by microinjections of DNQX versus mixture (D1/D2/DNQX). Appetitive eating behavior (green symbols) was stimulated by DNQX microinjections in the rostral shell, whereas fearful defensive treading was elicited by caudal DNQX microinjections (red symbols; criteria for including a DNQX site was a >9 min increase in eating duration plus a >200% increase in food intake for appetitive effects, and >20 s duration and >400% increase in defensive treading behavior; both compared with vehicle microinjection at same site). Histogram bars express the percentage change in behaviors from vehicle levels [eating duration (in minutes); defensive treading duration (in seconds)]. Addition of D1 and D2 receptor antagonists in the mixture condition blocked the ability of DNQX to generate either eating or defensive behavior at most sites (right).