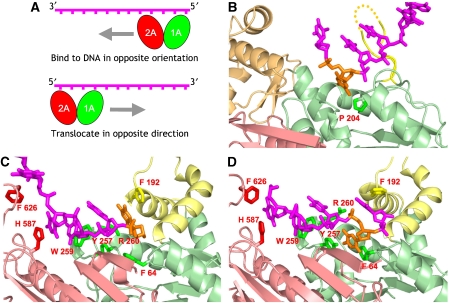
Figure 3.
(A) Two models for ways to convert helicase directionality from 3′–5′ to 5′–3′. The panel at the top shows the DNA bound in the reverse orientation, whereas the panel below shows the alternative in which translocation is reversed instead. (B) Location of the motif 1a pocket in RecD. The base in the pocket is coloured orange. Other colours follow the same scheme as Figure 2. (C) The equivalent view of the PcrA substrate complex (Velankar et al, 1999). Note that in this structure, the motif 1a pocket is blocked by F64. (D) The equivalent view of the PcrA product complex (Velankar et al, 1999). In this structure, the motif 1a pocket is open because F64 has swung out of the way allowing a DNA base (shown in orange) to occupy the pocket.