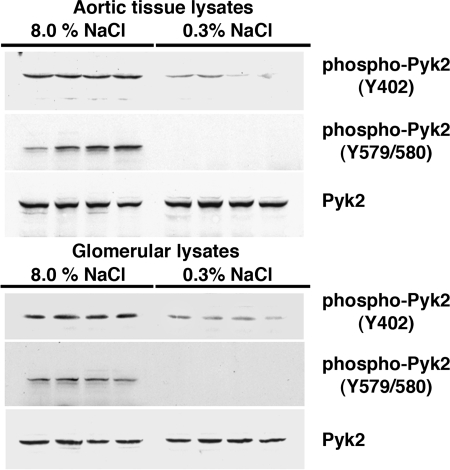
Fig. 1.
Western analyses of the effect of salt intake on the phosphorylation state of proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2 (Pyk2) in lysates from aortic tissue (top) and isolated glomeruli (bottom). Although total levels of Pyk2 did not differ between the 2 groups, compared with rats on the 0.3% NaCl diet, rats on the 8.0% NaCl diet demonstrated increased levels of phospho-Pyk2(Y402), represented as the ratio of density of phospho-Pyk2(Y402) to the density of total Pyk2 in lysates of aortic tissue (0.63 ± 0.03 vs. 0.14 ± 0.02; P < 0.05) and isolated glomeruli (0.708 ± 0.10 vs. 0.06 ± 0.04; P < 0.05). Levels of phospho-Pyk2(Y579/80)/total Pyk2 in both aortic tissue lysates (0.56 ± 0.11 vs. undetectable; top) and glomerular lysates (0.58 ± 0.08 vs. undetectable; bottom) were also dramatically increased in rats on the 8.0% NaCl diet. Immunoblot analysis of phospho-Pyk2(Y881) was performed but was not observed in either group (data not shown). Each column represents data from the same rat (n = 4 rats/group).