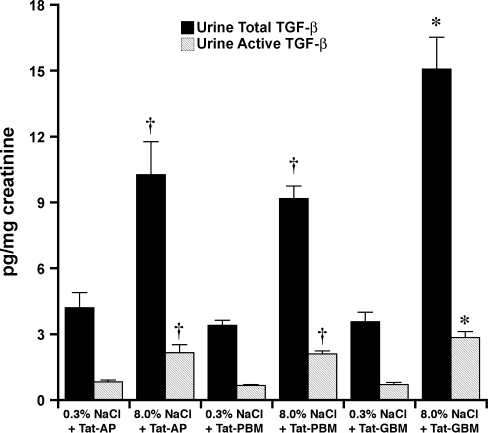
Fig. 8.
Effect of a single intravenous injection of the Tat fusion proteins (2.5 μM) on subsequent urinary excretion of total TGF-β and active TGF-β. Urine was obtained the day after the intravenous injection. Although the excretion rates did not fall to levels observed in rats on the 0.3% NaCl diet, the increases in urinary total and active TGF-β that occurred in response to increased salt intake were inhibited by intravenous injection of Tat-AP and Tat-PBM (n = 4 rats in each group). *P < 0.05 compared with the other 5 groups. †P < 0.05 compared with the groups of rats that received the 3% NaCl diet and the Tat fusion proteins.