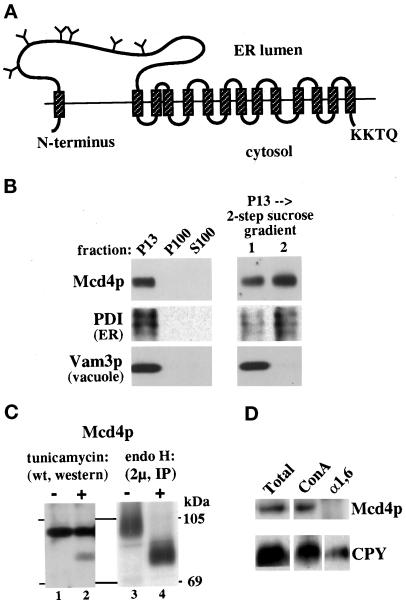
Figure 1.
Mcd4p is an ER-localized, multimembrane-spanning protein with a large, lumenal N-terminal domain. (A) Predicted topology of Mcd4p in the ER membrane, based on data shown in panels B, C, and D. Predicted TMDs (hatched boxes), N-linked glycosylation sites likely to be utilized (Y), and the C-terminal KKXX motif are shown. (B) Subcellular localization of Mcd4p. Wild-type (SEY6210) cells were spheroplasted and subjected to differential centrifugation. The 13,000 × g pellet (P13) was further resolved on a two-step sucrose gradient. Shown are the immunoblots of the P13, P100, and S100 fractions for Mcd4p (1:150), PDI (1:320), and Vam3p (1:2500). (C) N-linked glycosylation of Mcd4p. Lanes 1 and 2: wild-type (SEY6210) cells were either treated with tunicamycin (+) or mock-treated (−) for 30 min, lysed, and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Mcd4p was visualized by immunoblotting. Lanes 3 and 4: wild-type cells overexpressing Mcd4p (SEY6210 harboring yEpMCD4) were pulse labeled, chased, and lysed. Mcd4p was recovered by immunoprecipitation and either treated with endo H (+) or mock-treated (−). The positions of molecular mass markers are shown to the right. (D) Post-ER modification of Mcd4p. Lysates were generated from wild-type (SEY6210) cells; 5 OD-eq of cells were prepared for immunoprecipitation with anti–α1,6-mannose antiserum (2 μl/OD) or precipitation with ConA-Sepharose; 1 OD-eq of total lysate (Total), and 2.5 OD-eq of ConA-Sepharose (ConA) and α1,6-mannose antiserum precipitates (α1,6) were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and Mcd4p (1:150) and CPY (1:5000) were visualized by immunoblotting.