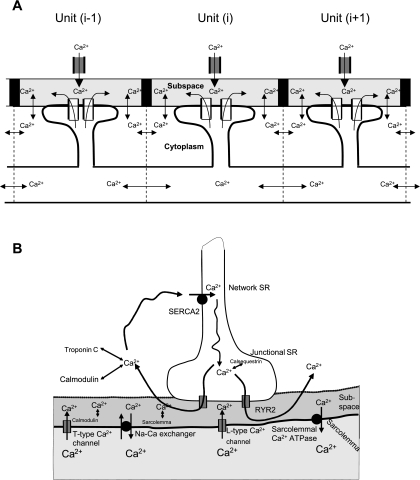
Fig. 1.
A: schematic model of a cluster of coupled ryanodine receptors (RyRs) in a cardiac cell. The cell has a length of 150 μm, with 75 elements, giving 2-μm spatial resolution. Coupling of these elements is via Ca2+ diffusion between neighboring cytoplasmic and network sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) spaces, as described in the appendix. B: schematic model of Ca2+ cycling for each element of the cluster illustrated in A. Three main Ca2+ cycling processes were modeled, which included 1) Ca2+ entry by L-type Ca2+ channel and Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR); 2) Ca2+ removal by Na/Ca exchanger and ATP-dependent Ca2+ pump; and 3) Ca2+ diffusion and Ca2+ binding to its buffers.