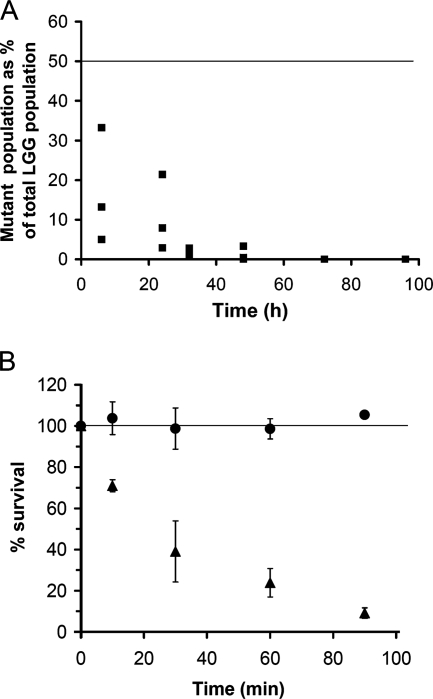
FIG. 2.
Characterization of the GIT survival capacity of luxS mutant strain CMPG5412. (A) Comparison of the wild-type control versus luxS mutant strain CMPG5412 for recovery in fecal samples. Mixtures of the wild-type control (CMPG5340) and mutant strain CMPG5412 (1:1) were administrated to three mice, and the percentage of mutants in the total L. rhamnosus GG (LGG) population, compared to an initial ratio of 50%, in fecal pellets was determined at different time points. Values for individual mice are shown. The line indicates the initial ratio of 50% mutant to 50% wild type (1:1) in the total L. rhamnosus GG population administered to the mice. (B) Comparison of wild-type control strain CMPG5340 versus luxS mutant strain CMPG5412 for survival in simulated gastric juice. The number of viable cells in simulated gastric juice was determined by plating a dilution series at different time points and expressed as a percentage of the initial numbers of cells added; circles indicate the wild type, and triangles indicate mutant strain CMPG5412. Data are the means of triplicate experiments, and error bars indicate standard deviations. The line indicates that the viable cell count at the initial time point was taken as 100%.