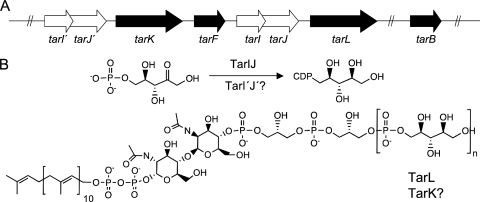
FIG. 1.
Poly(ribitol phosphate) synthesis in S. aureus. (A) The region of the S. aureus chromosome involved in ribitol phosphate polymer synthesis for cell wall teichoic acid contains a putatively duplicated gene cluster (tarI′J′K and tarIJL). The genes in this region encode the enzymes involved in CDP-ribitol synthase (TarI′J′ and TarIJ), denoted by the white arrows, and genes involved in glycerol phosphate (TarB and TarF) and ribitol phosphate (TarK and TarL) transferase activities, denoted by the black arrows. The gene tarF, encoding a glycerol phosphate transferase, separates the two gene clusters. (B) Cell wall teichoic acid is assembled on the membrane-bound prenyl-linked disaccharide. The activities of the ribitol phosphate transferases and the CDP-ribitol synthase enzymes are indicated. It is unknown if TarI′J′ and TarK are capable of efficiently catalyzing their predicted functions.