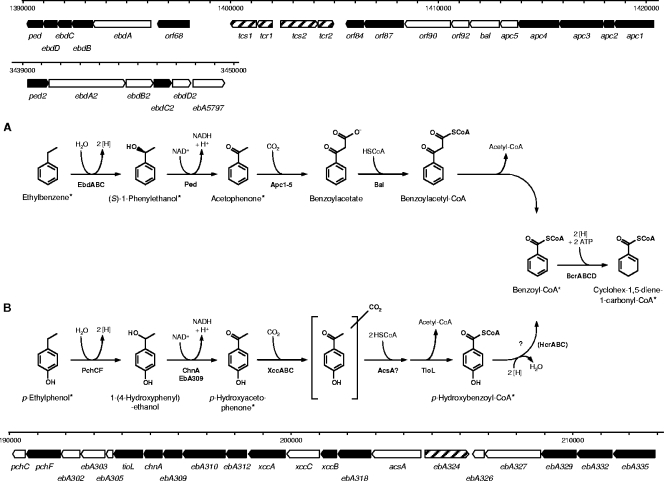
FIG. 1.
Anaerobic degradation pathways of ethylbenzene (A) and p-ethylphenol (B) in “A. aromaticum” strain EbN1. The two initial reactions are chemically analogous but involve different enzymatic catalysis. Both pathways converge at the common intermediate benzoyl-CoA (the ethylbenzene pathway is modified from reference 37). Enzyme names of the indicated gene products (shown in bold type) are as follows: Apc1-5, acetophenone carboxylase; AcsA, predicted acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase; Bal, benzoylacetate CoA-ligase; BcrABCD, benzoyl-CoA reductase; ChnA, predicted cyclohexanol dehydrogenase; EbA309, putative alcohol dehydrogenase; EbdABCD, ethylbenzene dehydrogenase; HcrABC, p-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase; Ped, (S)-1-phenylethanol dehydrogenase; PchCF, predicted p-ethylphenol methylhydroxylase; TioL, predicted thiolase; XccABC, predicted p-hydroxyacetophenone carboxylase. A scale model for the organization of the involved genes is displayed for both pathways. In addition, the paralogous gene cluster for the “upper part” of the alkylbenzene degradation pathway is shown. The scale bar indicates the locations of the genes on the chromosome by the nucleotide positions. Products of genes marked in black were identified on the 2D DIGE gels. *, compounds identified by GC-MS analysis.