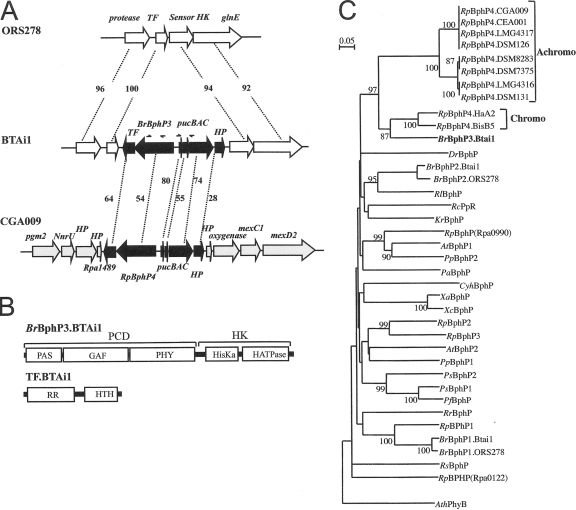
FIG. 1.
Molecular characterization of BphP3B BTAi1. (A) Comparative genomic analysis of the region surrounding the pucBA operon and BphP3B BTAi1 (BrBphP3) in the Bradyrhizobium BTAi1 and ORS278 strains and in R. palustris CGA009. The values given between the genes correspond to the percentages of identity of the corresponding proteins. The arrows indicate the localization of the primers used to search for pucBA and BphP genes in different photosynthetic bradyrhizobia. Abbreviations: TF, transcriptional factor; HP, hypothetical protein. (B) Predicted domain structure of BphP3B BTAi1 (BrBphP3.BTAi1) and TFBTAi1 (TF.BTAi1). HK, histidine kinase domain; HisKa, phosphoacceptor domain; HATPase, ATP binding domain; RR, response regulator domain; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of the BphP family based on an alignment of the GAF domain. The sequences were aligned by using the CLUSTALX software program, and the tree was generated by the neighbor-joining method and displayed using the NJPLOT software program. Bootstrap values, expressed as percentages of 1,000 replications, are given at the branching points. The end points of the GAF domain of each sequence were determined by Pfam analysis (1). Species abbreviations: At, Agrobacterium tumefaciens; Ath, Arabidospsis thaliana; Br, Bradyrhizobium sp.; Dr, Deinococcus radiodurans; Pa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Pf, Pseudomonas fluorescens; Pp, Pseudomonas putida; Ps, Pseudomonas syringae; Rc, Rhodospirillum centenum; Rl, Rhizobium leguminosarum; Rp, R. palustris; Rr, Rhodospirillum rubrum; Rs, Rhodobacter sphaeroides; Xa, Xanthomonas axonopodis; Xc, Xanthomonas campestris.