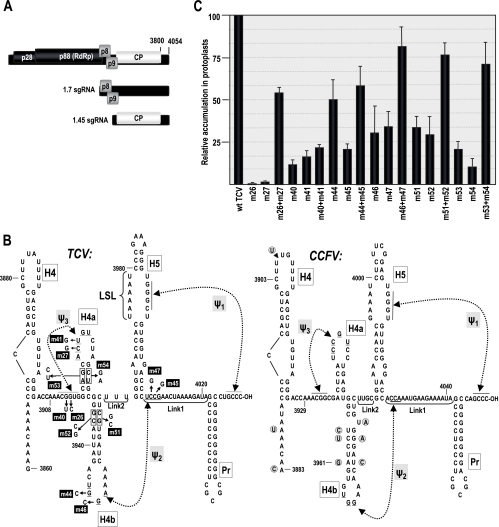
FIG. 1.
Genomic organization and 3′ UTR RNA structures in TCV. (A) TCV genomic and subgenomic RNAs encode proteins involved in replication (p28 and p88), movement (p8 and p9), and encapsidation/RNA silencing suppression (CP). Carmoviruses CCFV and JINRV have similar genomic arrangements, but open reading frames have not been analyzed. (B) Structure of the 3′-terminal regions of TCV (left) and CCFV (Blue Lake strain) (right). H5 and Pr hairpins are conserved in nearly all carmoviruses. Ψ1 is also conserved among carmoviruses and was previously shown to exist for TCV in vivo (46). H4a, H4b, and Ψ3 in TCV were predicted by MPGAfold. Ψ2 forms in the preactive structure of satC (44). Mutations constructed to examine the existence of these elements in TCV and their numeric designations are shown. Base differences found in the CCFV Clear Lake strain are circled. Putative CCFV elements are designated according to analogous structures in TCV. (C) Accumulation of mutant TCV in protoplasts at 40 hpi. All values were averages from at least three experiments. Standard deviation bars are indicated.