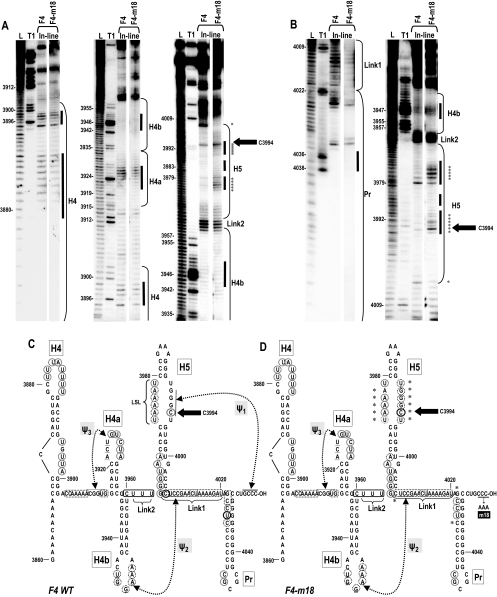
FIG. 2.
In-line probing of the 3′ UTR region of TCV. (A) In-line probing of fragments containing wt TCV and TCV with a 3′-terminal CCC-to-AAA alteration (TCV-m18). F4 fragments (positions 3860 to 4054 [H4→3′ end]) were 5′ end labeled (A) or 3′ end labeled (B) and incubated at 23°C for 14 h before gel electrophoresis. Left panels, 20% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; center and right panels, 8% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. L, ladder generated by nonspecific partial cleavages; T1, ladder generated by partial RNase T1 digests using partially denatured RNA; F4, F4 fragment; F4-m18, F4-m18 fragment. Locations of the hairpins, Link1, and Link2 are indicated. Bars indicate predicted terminal and internal loops within the hairpins. Positions of selected guanylates are given. Asterisks denote cleavage differences between wt F4 and F4-m18. The large black arrow denotes the location of C3994, which is strongly susceptible to in-line cleavage. This susceptibility to in-line cleavage was also predicted by MD simulations (see text and Fig. 5). (C) Position of residues cleaved by in-line probing in wt F4. Circled bases were susceptible to cleavage. Darker circles indicate a higher level of spontaneous cleavages relative to other cleavages. Hairpin and pseudoknot designations are as shown in Fig. 1B. (D) Position of residues cleaved by in-line probing in F4-m18. The altered bases that comprise the m18 mutation are indicated. Asterisks denote cleavage differences between wt F4 and F4-m18. (C and D) The location of C3994 is denoted by large black arrows.