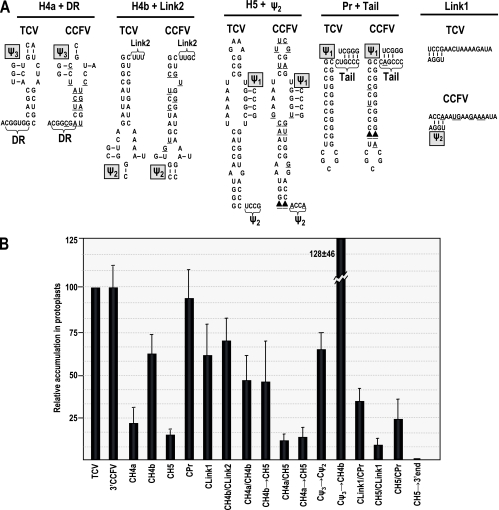
FIG. 3.
Stepwise replacements of TCV elements with analogous regions from CCFV reveal functional domains. (A) Comparison of sequences comprising elements of TCV and CCFV. Underlined bases in the CCFV sequences denote differences from TCV. Putative Ψ3, Ψ2, and Ψ1 that could form when CCFV sequences are partnered with TCV background sequences are shown. The wt TCV pseudoknot pairings are also shown. Filled triangles denote missing bases. Locations of the hairpins, pseudoknots, and linker (Link) sequences are shown in Fig. 1B. The DR sequence was previously identified in satC as being a sequence-specific element required for the conformational switch between preactive and active structures (44). (B) Relative accumulation of chimeric TCV RNAs in protoplasts at 40 hpi compared with that of parental TCV-TSNLS (TCV) as assayed by RNA gel blots using a TCV-specific probe. The composition of the replacement elements is given, preceded by a “C” for CCFV. Results are the average of three experiments. Standard deviation bars are shown. 3′CCFV, 142 nt at the 3′ terminus of CCFV.