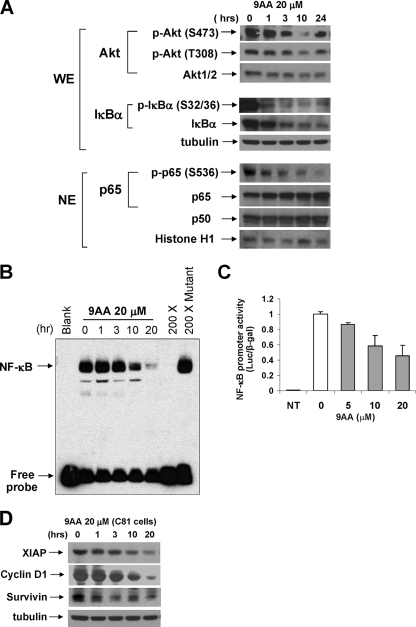
FIG. 5.
9AA inhibits NF-κB activation in HTLV-1 cells. (A) Whole-cell extract (WE; 100 μg) was immunoblotted with phospho-Akt or phospho-IκBα. Nuclear extract (NE; 100 μg) was immunoblotted with phospho-p65 (S536) antibodies, p65 or p50. β-Tubulin or histone H1 was used as a loading control. (B) Effect of 9AA on NF-κB DNA binding activity was assessed by EMSA using a consensus NF-κB oligonucleotide probe. C8166 cells were treated with 9AA, and nuclear extracts were prepared. For the competition assay, a 200 molar excess amount of unlabeled consensus or mutated consensus was used. (C) C8166 cells were transfected using Transfast reagent (Promega) with 5×NF-κB-Luc (0.5 μg). Three hours posttransfection, the cells were treated with 9AA (0, 5, and 10 μM). Cells were harvested 24 h later, and luciferase (Luc) activities were measured. The luciferase value was adjusted by CMV-β-galactosidase (β-gal) activity. Error bars represent the standard deviations of three independent experiments. (D) To examine cellular genes which are regulated by NF-κB, cell extracts from 9AA (20 μM)-treated C8166 (C81) cells were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-XIAP, anti-cyclin D, and anti-survivin antibodies. β-Tubulin was used as an internal loading control. NT, not treated.