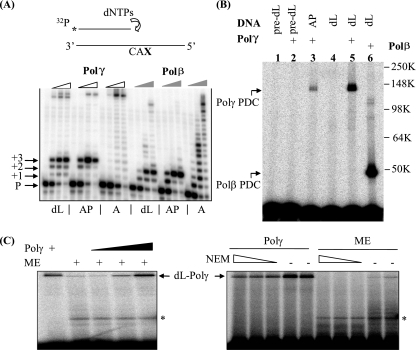
FIG. 1.
The oxidative DNA lesion dL blocks DNA synthesis by Polγ and inactivates the enzyme by forming a covalent DNA-protein cross-link during attempted SP-BER. (A) A running-start experiment was performed to investigate the effect of dL or an AP site on Polγ-mediated DNA synthesis. The reactions were performed with proofreading-deficient Polγ holoenzyme (indicated by open wedges) and Polβ (indicated by filled wedges). In the schematic drawing, CAX in the template strand indicates the sequence: C and A nucleotides followed by an abasic residue (dL or AP) or an undamaged adenylate nucleotide (A). P, +1, +2, and +3 indicate, respectively, the labeled primer and the extension products with one, two, or three additional nucleotides. The full-length extension products appear near the top of the images and are most readily seen with the undamaged A substrate (see designations below the panel). dNTPs, dinucleotide triphosphates. (B) dL traps purified Polγ. A 3′-end-labeled, nicked-DNA duplex with a 5′ dL in the gap was used to mimic the repair intermediate after Ape1 incision. The protein-DNA complex (PDC) of Polγ formed with an incised AP site and reductive trapping with NaBH4 (37) is shown in lane 3. pre-dL, the dL precursor. Molecular weights in thousands (K) are listed on the right of the gel. (C) dL traps Polγ in ME. A protein-DNA cross-link band was detected with ME of HeLa cells and migrated identically to the recombinant Polγ marker, which was also titrated into the extract for the right three lanes of the left panel. Upon treatment with N-ethylmaleimide (NEM; 5, 10, and 20 mM), this high-molecular-weight band disappeared, consistent with the sensitivity of Polγ to this reagent. The identity of the lower band seen with ME (indicated by an asterisk) is unknown, and it may result from dL cross-linking with contaminating Polβ, a proteolytic fragment of Polγ, or other unidentified mitochondrial proteins with dRP lyase activity.