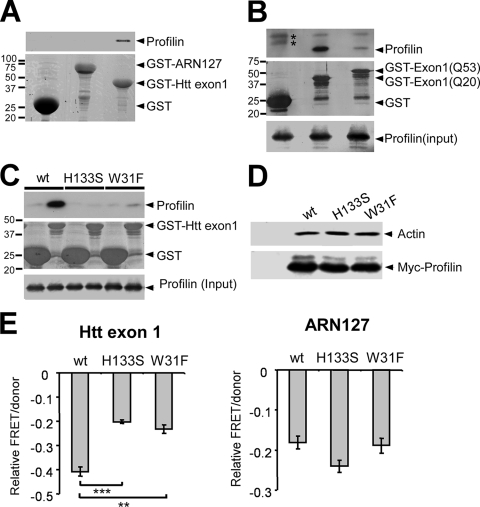
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of Htt aggregation by profilin requires direct interaction. (A) Sepharose-bound GST, GST-ARN127(Q25) YFP, or GST-Htt exon 1(Q25) was mixed with bacterial lysate containing His-profilin. GST-Htt exon 1(Q25) interacted with His-profilin, whereas GST and GST-ARN127(Q25) YFP did not. (B) Sepharose-bound GST, GST-Htt exon 1(Q20), or GST-Htt exon 1(Q53) was mixed with HEK293 cell lysate containing profilin. GST-Htt exon 1(Q53) bound 85% less profilin than GST-Htt exon 1(Q20). Asterisks indicate two bands nonspecifically reacting with the anti-profilin antibody. (C) Sepharose-bound GST or GST-Htt exon 1(Q25) was mixed with HEK293 cell lysate containing profilin(wt) or the polyproline binding mutants (H133S and W31F). Profilin(wt) bound GST-Htt exon 1(Q25), and the two mutants did not. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with untagged (first lane) or Myc-tagged profilin (wt, H133S, or W31F). Cell lysate was immunoprecipitated using an anti-Myc antibody, followed by Western blotting against actin. Polyproline binding-deficient profilin mutants bound amounts of actin similar to those of profilin(wt). (E) Profilin (wt, H133S, or W31F) was cotransfected into HEK293 cells with Htt exon 1(Q72) CFP/YFP or ARN127(Q65) CFP/YFP. Relative aggregation was measured by FRET. Both mutants inhibited ARN127(Q65) aggregation comparably to profilin(wt) but were significantly less effective in inhibiting Htt exon 1(Q72) aggregation (***, P < 0.0005; **, P < 0.005 [unpaired t test]). Error bars represent the SEM.