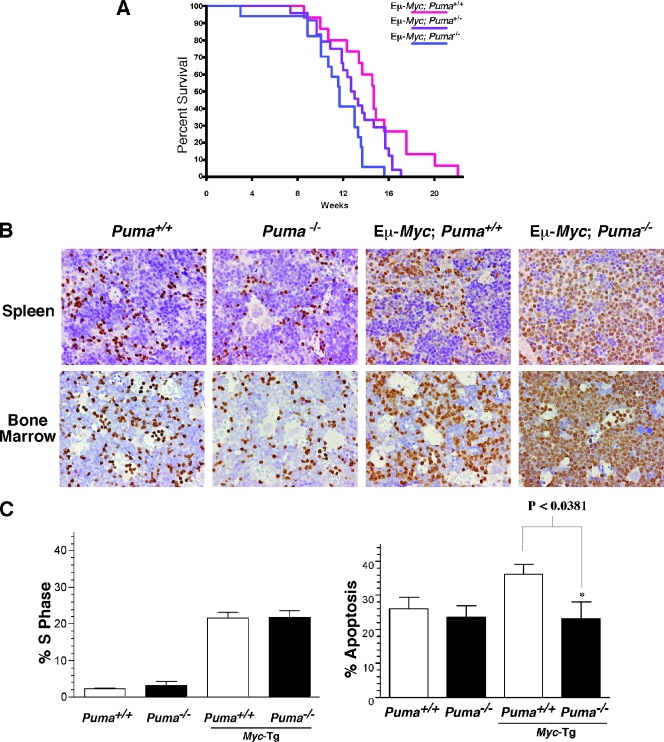
FIG. 2.
Puma deficiency accelerates Myc-induced lymphomagenesis. (A) Tumor-free survival of Eμ-Myc; Puma−/− (n = 17, blue), Eμ-Myc; Puma+/− (n = 24, purple), and Eμ-Myc; Puma+/+ (n = 15, red) animals. (B) Early infiltration of premalignant B cells in the spleens and bone marrow of Eμ-Myc; Puma−/− mice. Histology of spleen tissue (upper) and bone marrow (lower) from Puma+/+, Puma−/−, Eμ-Myc; Puma+/+, and Eμ-Myc; Puma−/− mice. Specimens were stained with the B-cell marker Pax-5 (data shown are representative of three independent experiments). (C) Puma deficiency protects against Eμ-Myc transgenic B-cell apoptosis without altering Myc-induced cell proliferation. Splenic B220+/IgM+ B cells from 7-week-old mice were analyzed by FACS for cell proliferation (left) and apoptosis (right) (n = 3 individual animals of each genotype).