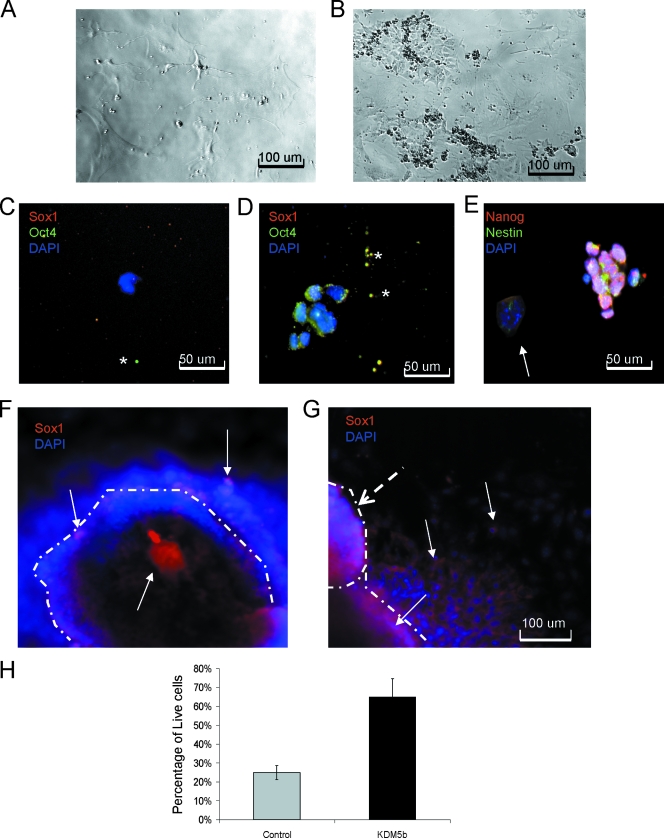
FIG. 6.
EBKDM5b retain highly proliferative cells that are refractory to differentiation. (A) Cells from dissociated normal EBs after four passages. (B) Cells from dissociated EBKDM5b after two passages. (C) Cells from dissociated normal EBs after two passages stained with DAPI (blue), Oct4 (green), and Sox1 (red). *, shows background spots. (D) Cells from dissociated EBKDM5b after four passages stained with DAPI (blue), Oct4 (green), and Sox1 (red). *, shows background spots (C and D). Cells from dissociated EBKDM5b after four passages stained with DAPI (blue), Nestin (green), and Nanog (red). (E) Arrow shows Nanog, Nestin double-negative colony of cells. (F) Neural differentiation of day 9 EBs from control; the edge of the colony is marked by a dashed line. Arrows show Sox1-positive (red) cells and DAPI-stained (blue) cells. (G) Neural differentiation of day 9 EBsKDM5b; the edge of the colony is marked by dashed lines. Dashed arrow shows secondary colony forming. Arrows show Sox1-positive (red) cells and DAPI-stained (blue) cells. (H) Graph of 7-amino-actinomycin D staining of cells found in media during neural differentiation of day 9 EBs from control (normal mESCs) and mESCKDM5b. The experiment was done in triplicate.