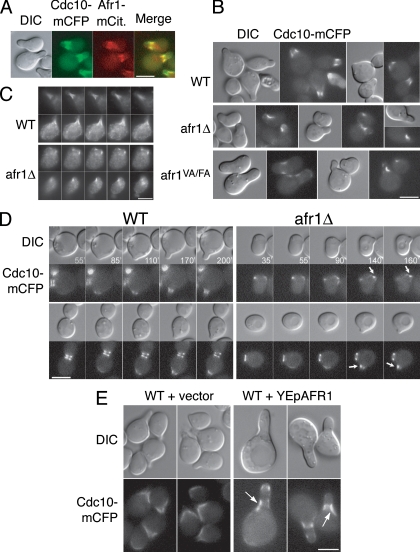
FIG. 6.
Afr1 regulates septin organization during mating. (A) Colocalization of Cdc10-mCFP and Afr1-mCitrine in strain JB251-10B. Differential interference contrast (DIC), fluorescence, and merged images are shown. Cdc10-mCFP and Afr1-mCitrine are pseudocolored green and red, respectively. (B) Cdc10-mCFP is asymmetric in AFR1 mutants. DIC and fluorescence images of wild-type (WT) (JB254-19C), afr1Δ (JB254-17C), and afr1VA/FA (JB255-8A) strains induced with α-factor are shown. (C) Cdc12 distribution is asymmetric in afr1Δ cells. Indirect immunofluorescence of Cdc12 with anti-Cdc12 antibody in WT (KT1193) and afr1Δ (JB66-2D) strains was performed. Images from five consecutive focal planes, 0.5 μm apart, are shown. (D) Time lapse microscopy of Cdc10-mCFP in WT (JB254-19C) and afr1Δ (JB254-17C) cells placed on agarose pads containing α-factor. (E) Cdc10-mCFP distribution in AFR1-overexpressing cells. Strain JB250-12B was transformed with pRS425 or pJK52. Transformants were treated with α-factor and visualized as described in Materials and Methods. DIC and fluorescence images are shown. Bars, 5 μm. Arrows indicate aberrant septin localization.