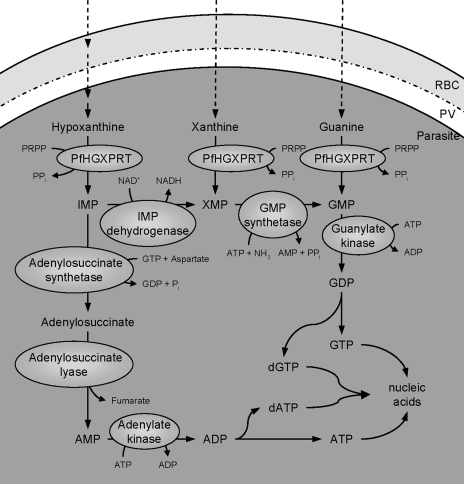
FIG. 2.
Nucleotide production in P. falciparum. Hypoxanthine, which is both transported into the cytoplasm from plasma and produced from adenosine and inosine metabolism (indicated by multiple arrows; see Fig. 1 for more detail), is converted to IMP by PfHGXPRT. IMP can then be converted to adenylate or guanylate nucleotides. To make adenylate nucleotides, IMP is converted to adenylosuccinate by adenylosuccinate synthetase. Adenylosuccinate lyase then converts adenylosuccinate to AMP. AMP is phosphorylated to ADP (by adenylate kinase). Alternatively, IMP can be converted to XMP by IMP dehydrogenase. XMP (which can also be produced directly from xanthine by PfHGXPRT) is converted to GMP by GMP synthetase. GMP can also be produced from guanine by PfHGXPRT. Guanylate kinase phosphorylates GMP to form GDP. Both GDP and ADP are then converted to the NTP or deoxynucleoside triphosphates used in nucleic acid synthesis. PRPP, phosphoribosylpyrophosphate; RBC, red blood cell; PV, parasitophorous vacuole.