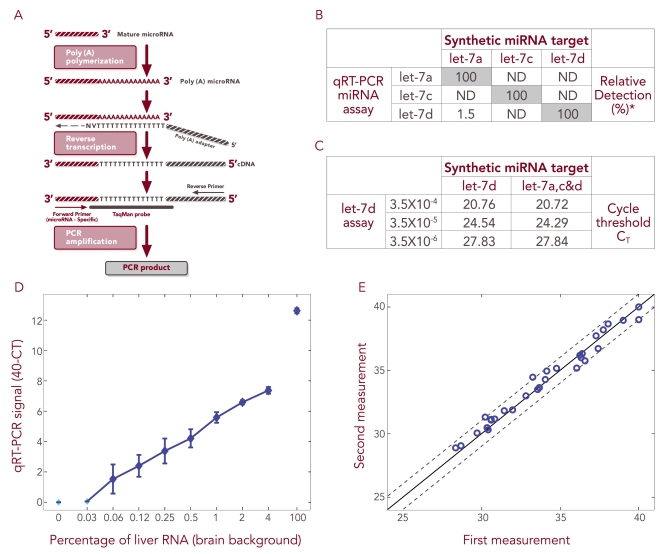
Figure 1. qRT-PCR can be used to monitor low microRNA levels specifically and sensitively.
A) Schematic representation of the qRT-PCR method. RNA is subjected to polyA polymerase reaction. Then, a universal RT reaction is performed that allows the amplification of all microRNAs as well as mRNAs. The PCR amplification is performed using a reverse primer complementary to part of the oligodT primer and a forward primer, which is homologous to a stretch in the microRNA sequence; in addition, the amplification reaction contains a TaqMan probe that covers part of the oligodT primer sequence and some nucleotides complementary to the 3′ sequence of the microRNA. B) Each synthetic RNA (hsa-let 7a, c & d) was subjected to three independent qRT-PCR amplifications, where in each reaction there were present primers specific to only one of the three family members. PCR amplification was observed only in the reaction where the primer matches the synthetic RNA. RNA amounts are described as percentages, each relative to the level observed in the reaction containing primers matching the synthetic microRNA. ND is non-detectable. C) All three synthetic microRNAs were mixed and subjected to qRT-PCR in the presence of the let-7d primer-probe set. In parallel, the same amount of synthetic let-7d as used in the mixture was subjected alone to qRT-PCR. These parallel PCR reactions were repeated using reducing concentrations of let-7d synthetic microRNA. At all tested concentrations of let-7d, it was amplified equivalently whether alone or in the presence of homologous family members. The CT of let-7d is proportional to the input microRNA amount. D) Reducing concentrations (100-0.03%) of total RNA extracted from liver tissue (Ambion Inc., No. 0360093B#) were mixed with total RNA extracted from brain tissue (Ambion Inc., No. 016P040305030A#) and the mixtures subjected to qRT-PCR, where each reaction contained a primer specific to hsa-miR-122a. Hsa-miR-122a was detected linearly, even in samples where only 0.03% liver RNA was spiked into brain RNA. When no liver RNA was introduced (100% brain RNA), hsa-miR-122a was not detected. E) The amounts of 32 different microRNAs in an RNA sample were examined on two independent occasions (by two different researchers) using the qRT-PCR platform (microRNA level is represented as CT value). The two profiles were within less than 1 CT difference of one another.