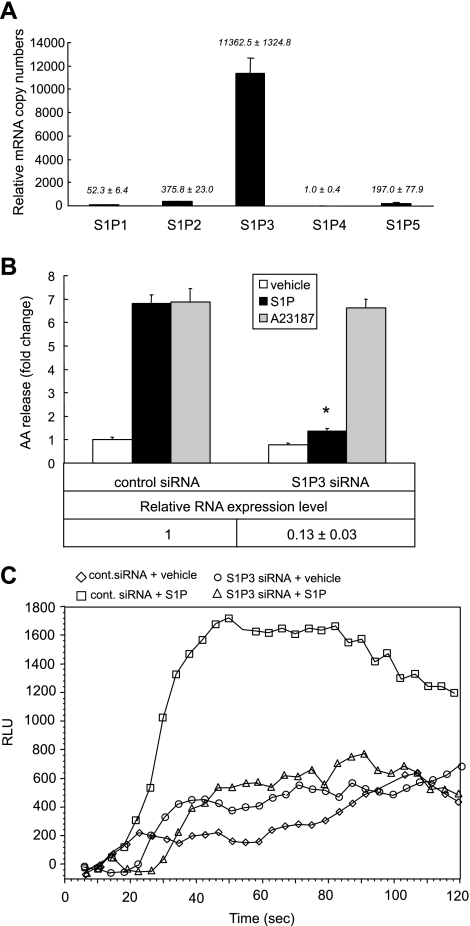
Fig. 5.
S1P signals through S1P3 to induce calcium mobilization and AA release. Relative expression levels of S1P receptors (S1P1–5). Total RNA was extracted from cells after 48-h culture. Real-time PCR was performed to detect the relative expression levels of five S1P receptors compared with internal control of GAPDH gene expression (A). A549 cells were transfected with S1P3 siRNA or negative control sequence in 12-well plates for AA release, 96-well plates for calcium flux assay, and 6-well plates for real-time PCR analysis. Cells were treated with S1P (500 nM), A23187 (100 nM), or vehicle for 10 min. The AA release is presented as fold change compared with the vehicle-stimulated control cells (B, top). The downregulation of S1P3 is presented as fold change compared with negative control sequence transfected cells by real-time PCR (B, bottom). The calcium flux assay was performed in S1P3 siRNA-treated or control siRNA-treated cells in 96-well plates, with and without stimulation with 500 nM S1P (C, □: control siRNA-treated cells with S1P; ◊: control siRNA-treated cells with vehicle; ○: S1P3 siRNA-treated cells with vehicle; and ▵: S1P3 siRNA-treated cells with S1P). The AA release data represent the means ± SD of 6 samples from a single experiment representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.0001 compared with control cells treated with S1P by Student's t-test. Real-time PCRs were done in triplicate in 2 independent experiments.