FIG. 3.
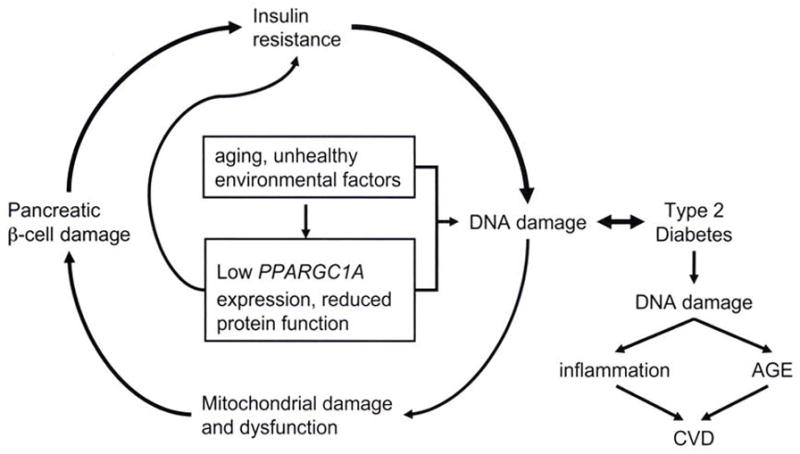
Cycle of DNA damage and type 2 diabetes, Aging and unhealthy environmental and genetic factors initiate DNA damage, which leads to damage of mitochondria, pancreatic β-cells, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and further DNA damage. Reduced expression of the PPARGC1A gene or function of the encoded protein is also linked to greater DNA damage. Eventually, repeated cycling through this process may result in type 2 diabetes, which produces greater damage of mtDMA. This can be the cause of inflammation and induction of AGE, leading to CVD.
