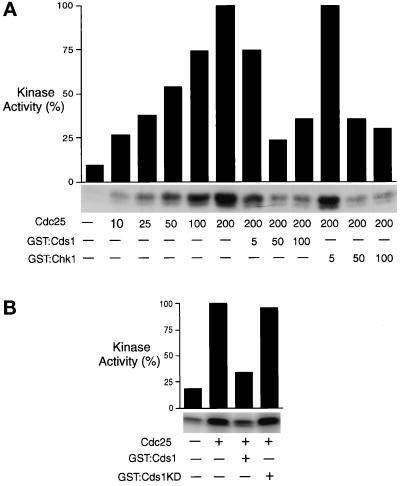
Figure 2.
Cds1 and Chk1 inactivate Cdc25 in vitro. (A) Hexahistidine-tagged S. pombe Cdc25 was expressed and purified from insect cells and used to activate Cdc2/cyclin-B1 purified from HeLa cells arrested in early S phase with thymidine. Antibodies to human cyclin-B1 were used to purify Cdc2/cyclin-B1 that was assayed by its ability to transfer [γ-32P]ATP to histone H1. Cdc25 was purified from 1 × 107 cells and suspended in 1 ml. Numbers in the Cdc25 row refer to the volume of Cdc25 preparation added to the reaction (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). Cdc25 caused a dose-dependent activation of Cdc2/cyclin-B. GST–Cds1 and GST–Chk1 were purified from fission yeast and used to phosphorylate Cdc25 before incubation with Cdc2/cyclin-B (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). Numbers in the GST–Cds1 and GST–Chk1 rows refer to the volume added of a 660-μl preparation made from 20 OD600 of cells. GST–Cds1 and GST–Chk1 caused a dose-dependent inhibition of Cdc25. The graph presents phosphorimager analysis of the autoradiogram shown below the graph. (B) The Cdc25 assay described above was repeated with GST–Cds1KD (GST–Cds1D312E), a kinase-inactive form of Cds1. Relative to active GST–Cds1, GST–Cds1KD only modestly decreased activation of Cdc2/cyclin-B by Cdc25. Coomassie blue staining confirmed that equal amounts of GST–Cds1 and GST–Cds1KD were added to these reactions (see Figure 3).