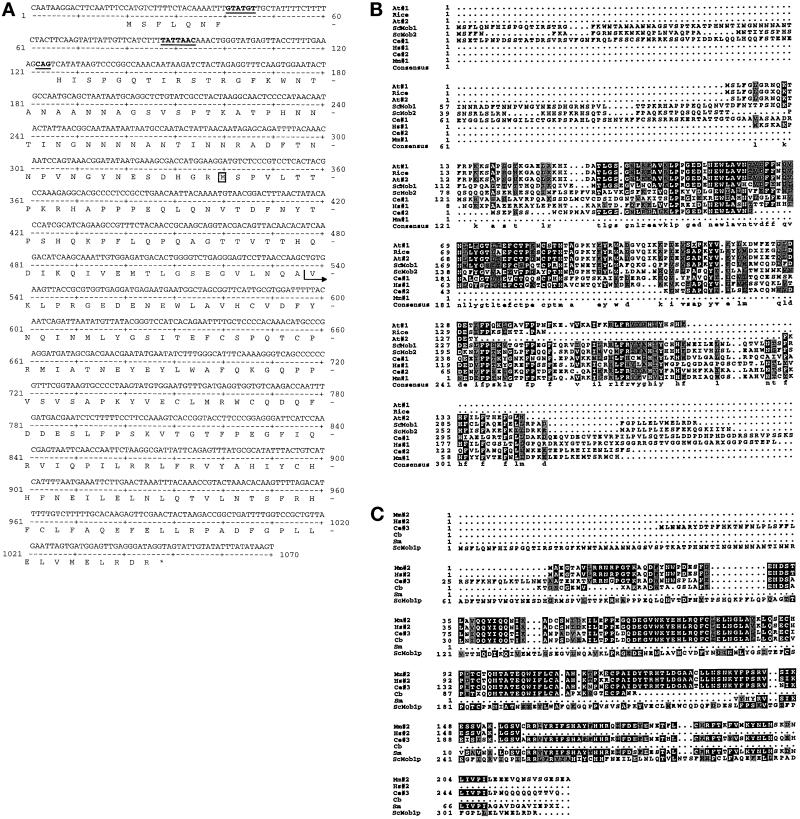
Figure 1.
MOB1 sequence analysis. (A) MOB1 DNA sequence and ORF. Underlined sequences represent the donor, branch, and acceptor sites for mRNA splicing. Note that the branch site is noncanonical. The postion of the initiator methionine of an unspliced MOB1 is boxed. The arrow indicates the fusion junction in the two-hybrid prey plasmid. (B) Aligned sequences of a subset of class 1 Mob1p-related ORFs from various genome databases. Comparison of Mob1p (ScMob1) and Mob2p (ScMob2) to predicted amino acid sequences from A. thaliania (At#1 represents a contig of GenBank accession numbers H77164 and T04732; At#2, GenBank accession no. Z46539); Rice (GenBank accession no. C19722); human (Hs#1 represents a contig of GenBank accession numbers F11288, F11866, R19220, R13096, and R59435); mouse (Mm#1, GenBank accession no. AA118366); and C. elegans (Ce#1, GenBank accession no. Z69788; Ce#2, GenBank accession no. Z77660). Sequences shaded in black are identical. Sequences shaded in gray are conserved. X’s represent ambiguous sequence. Note that many of the sequences derive from expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and therefore may be incomplete. (C) Aligned sequences of a subset of Class 2 Mob1p-related ORFs from various genome databases. Mob1p (ScMob1) sequence is compared with predicted amino acid sequences of the class 2 Mob1p-related sequences isolated from mouse (Mm#2 represents a contig of GenBank accession numbers U01138, AA125007, and AA208960); human (Hs#2 represents a contig of GenBank accession numbers W76032, D59087, N55945, and T79518); C. elegans (Ce #3, GenBank accession no. L10990); C. briggsae (Cb, GenBank accession no. R03084); and S. masoni (Sm, GenBank accession no. AA1468).