Figure 4. Mechanism of action of MxA.
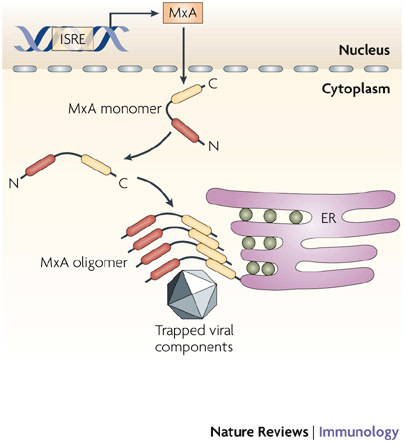
Following stimulation with type I interferons (IFNs), MXA (myxovirus-resistance A) gene expression is induced through an IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) in the gene promoter. The MxA protein accumulates in the cytoplasm on intracellular membranes (such as the endoplasmic reticulum, ER) as oligomers formed by association between the leucine zipper (LZ) domain and central interactive domain of the protein. Following viral infection, MxA monomers are released and bind viral nucleocapsids or other viral components, to trap and then degrade them.
