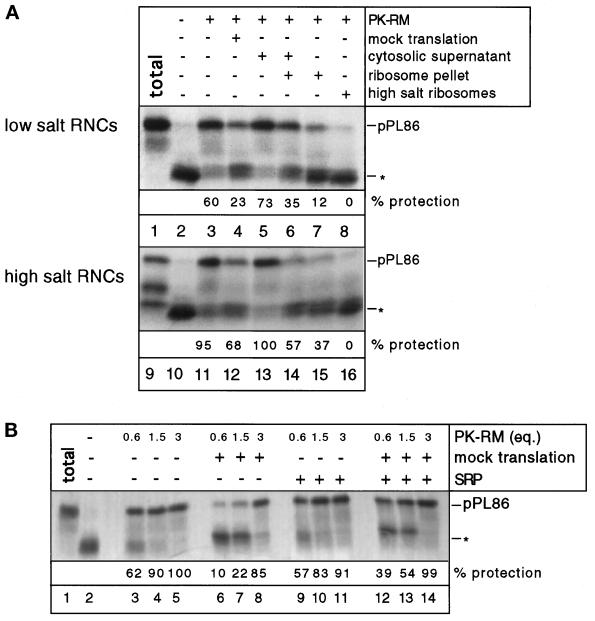
Figure 3.
Competition of RNCs with nontranslating ribosomes for membrane-binding sites. (A) Inhibition of SRP-independent targeting of isolated RNCs by ribosomes. pPL86 was synthesized in a wheat germ system and the RNCs were isolated under low- (150 mM) or high- (500 mM) salt conditions. As competitors, either a mock translation mixture was added or fractions containing the ribosome pellet or the cytosolic supernatant. In some experiments, ribosomes washed with high salt were used (high-salt ribosomes). Membrane binding to PK-RM was tested with a protease protection assay. Lanes 1 and 9 show the undigested pPL86 (total), all other samples were treated with proteinase K. Asterisk indicates the position of the ribosome-protected fragment of about 30 residues. (B) Dependence of targeting of RNCs on ribosomes and membrane-binding sites. pPL86 was synthesized in a wheat germ system and SRP was added where indicated. Some samples received a sixfold excess of a mock translation mixture. After addition of different amounts of PK-RM (given in Eq), membrane targeting was assayed by protease protection. Lane 1 shows the undigested pPL86 (total), all other samples were treated with proteinase K. Asterisk indicates the fragment of about 30 amino acids protected against the protease by the ribosome.