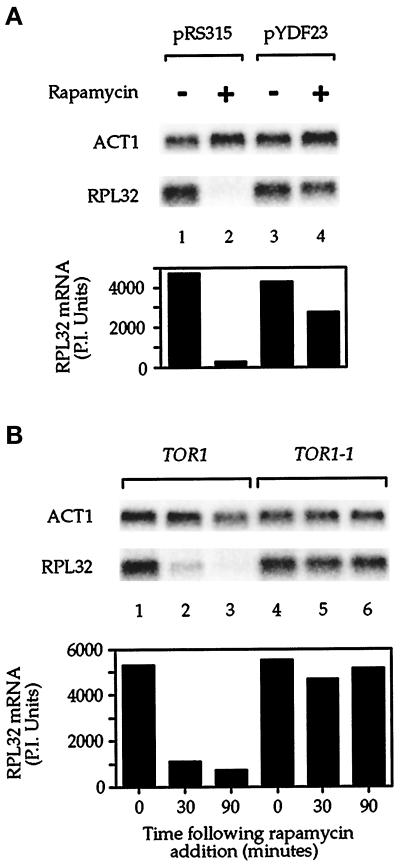
Figure 5.
The TOR pathway regulates r-protein mRNA levels. (A) Cells were transformed with a control plasmid (pRS315 [Sikorski and Heiter, 1989], lanes 1 and 2) or with a plasmid containing the TOR1-1 allele (pYDF23 [Zheng et al., 1995], lanes 3 and 4) and were grown in SC dextrose media lacking leucine to select for plasmid maintenance. Rapamycin was added as indicated, and cells were incubated for an additional 90 min. (B) Wild-type strain JH11-1c (lanes 1–3, TOR1) or TOR1-1 strain JK9-3da (lanes 4–6, TOR1-1) (Barbet et al., 1996) was grown to midlog phase in YPD and treated with rapamycin for the time indicated. In both A and B, cells were harvested after rapamycin treatment, total RNA was prepared, and the specified mRNAs were analyzed by Northern blotting (top). Quantitation of RPL32 mRNA levels is presented as phosphorimager units (P.I. Units), normalized to ACT1 mRNA (bottom).