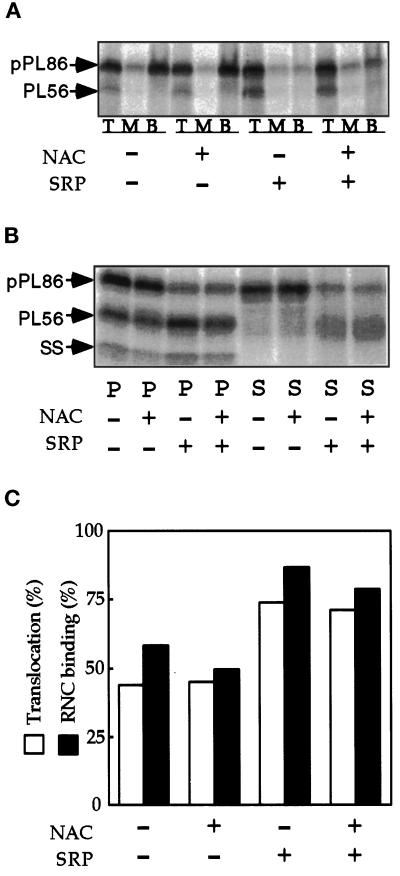
Figure 1.
SRP-dependent and SRP-independent binding of ribosomes to PK-RM. The pPL86 mRNA was translated in the presence or absence of SRP. RNCs or SRP-RNCs were isolated by centrifugation through a high-salt (500 mM KOAc) sucrose cushion to deplete NAC (-) or through a low-salt (150 mM KOAc) sucrose cushion to mock-deplete NAC (+). Aliquots (10 μl) of the SRP-RNCs (+SRP) and the RNCs (-SRP) were incubated for 5 min with 4 eq of PK-RM. GTP was only added to assays that contained SRP. Aliquots were removed for ribosome binding assays (panel A) and translocation assays (panel B). (A) To monitor binding of RNCs to PK-RM, the samples were adjusted to 2.1 M sucrose and applied as the bottom layer of a three-step discontinuous sucrose gradient (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). After centrifugation, membrane-bound pPL86 and PL56 were recovered in the top (T) and middle (M) fractions, while unbound pPL86 remained in the bottom (B) fraction. (B) To assay translocation, the samples were adjusted to 25 mM EDTA and incubated for 10 min at 25°C before centrifugation to separate PK-RM in the pellet (P) fraction from soluble components in the supernatant (S) fraction. Radioactive bands corresponding to pPL86, PL56 and the signal sequence (SS) are labeled. (C) The % RNC binding and the % translocation were calculated (see MATERIALS AND METHODS) after quantification of pPL86 and PL56 in the gels shown in panels A and B.