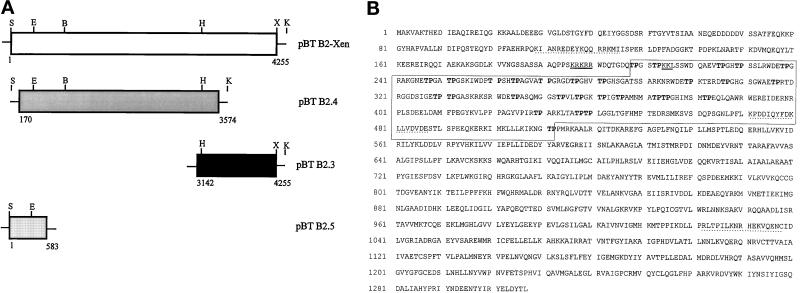
Figure 1.
Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a novel nuclear protein from X. laevis. (A) Schematic representation of the assembled pBT B2-Xen full-length cDNA and overlapping subclones (pBT B2.4; pBT B2.3; pBT B2.5) thereof. Partial restriction maps indicate the enzymes used for generating the full-length cDNA: S, SpeI; E, EcoRV; B, BamHI; H, HincII; X, XhoI; K, KpnI (see also MATERIALS and METHODS). Numbers give the nucleotide positions with reference to the assembled full-length cDNA. (B) Amino acid (aa) sequence deduced from cDNA clone pBT B2-Xen. The open reading frame comprises 1307 aa coding for a 146-kDa protein. An internal domain characterized by the presence of several TP-motifs (in bold letters) is denoted by a box (aa 208–512). A putative bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) is underlined, and sequences used for generating antibodies are marked by dotted lines.