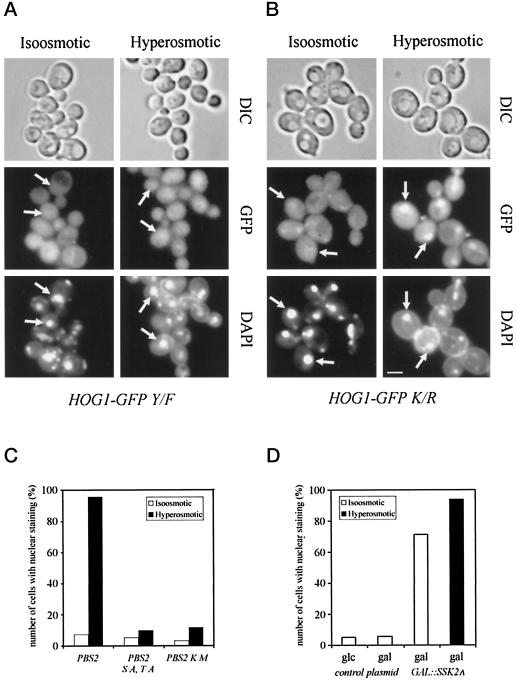
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation, but not kinase activity is necessary for nuclear accumulation of Hog1. Strain K4327 (hog1Δ) was transformed with centromer plasmids (A) pVR65–Y/F containing HOG1 phosphorylation site mutant allele (HOG1–GFP Y/F, HOG1 with T174F mutation) or (B) pVR65–K/R containing HOG1 catalytic site mutant allele (HOG1–GFP K/R HOG1 with K52R mutation). Transformants were grown to logarithmic phase in selective medium (iso-osmotic). Where indicated, strains were stressed for 5 min by addition of NaCl to a final concentration of 0.4 M (hyperosmotic). Positions of nuclei are indicated by arrows. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Hog1–GFP nuclear accumulation is dependent on active Pbs2 MAPKK. The following strains were analyzed: strain VRY 10 (pbs2Δ) cotransformed with pVR65–WT (HOG1–GFP) and pVR15 (PBS2, endogenous promoter), pVR20 (PBS2S/A, T/A; PBS2 with S174A and T178A mutations), and pVR15K/M (PBS2K/M; PBS2 with K389M mutation). (D) The overexpression of the Ssk2ΔN allele induces nuclear accumulation of Hog1–GFP in nonstressed cells. Strain K4327 (hog1Δ) was cotransformed with centromer plasmid pVR65–WT (HOG1–GFP) and plasmid pGSS21 (2 μm PGAL1-SSK2ΔN, SSK2 from M1173 to D1579). Cells were grown in appropriate selective medium containing raffinose as carbon source, washed with water, and resuspended in fresh selective medium with galactose or glucose as carbon source (iso-osmotic). Where indicated, cells were stressed with 0.4 M NaCl for 5 min before microscopy (hyperosmotic). glc, glucose; gal, galactose.