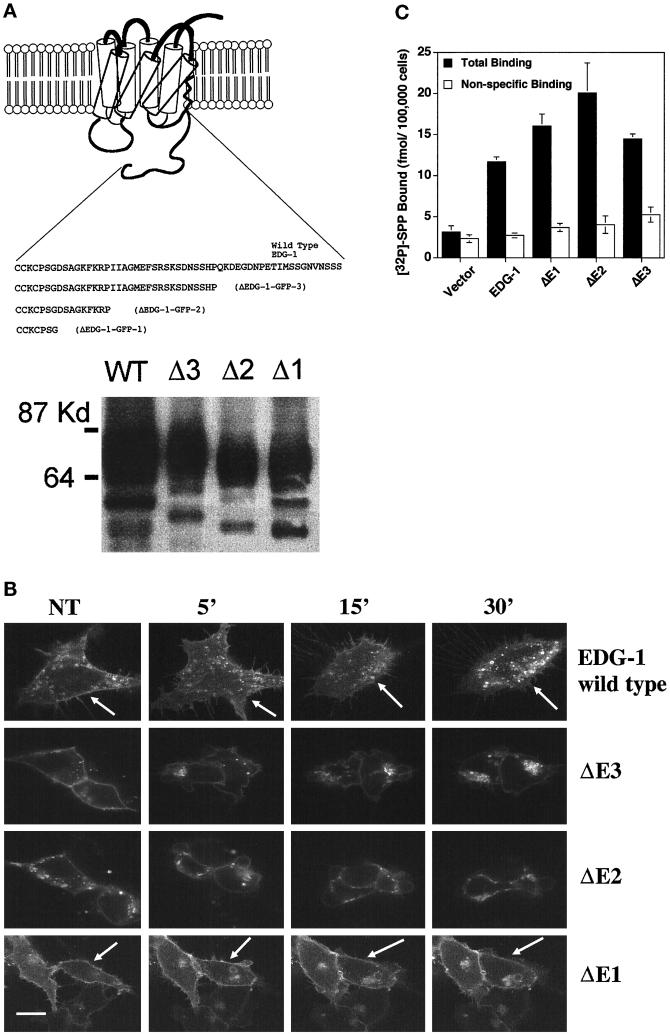
Figure 6.
C-terminal–deleted EDG-1–GFP chimeras. (A) Top, schematic representation of C-terminal–deleted EDG-1–GFP chimeras. Deleted ΔEDG-1 clones (1–3) were fused to the GFP polypeptide at the C terminus, and stable clones of HEK293 cells were derived as described. Bottom, the production of appropriately sized EDG-1–GFP and ΔEDG-1–GFP polypeptides determined by immunoblot analysis of cell extracts. Thirty micrograms of extract from the wild-type EDG-1–GFP (WT)-transfected cells and 10 μg from Δ3-, Δ2-, and Δ1-transfected cells were used. (B) SPP-induced internalization of ΔEDG-1–GFP chimeras. HEK293 cells stably transfected with EDG-1–GFP, ΔEDG-1–GFP-3 (ΔE3), ΔEDG-1–GFP-2 (ΔE2), and ΔEDG-1–GFP-1 (ΔE1) were treated with 100 nM SPP for the indicated times at 37°C and imaged by confocal microscopy. Note the reduction of plasma membrane fluorescence in the wild-type (indicated by arrows) and ΔE3-transfected cells but not in ΔE2 and ΔE1 cells (indicated by arrows). Bar, 10 μm. (C) Binding of [32P]SPP to HEK293 cells transiently transfected with EDG-1–GFP, ΔEDG-1–GFP-3 (ΔE3), ΔEDG-1–GFP-2 (ΔE2), and ΔEDG-1–GFP-1 (ΔE1).